Discovery and Validation of Novel microRNA Panel for Non-Invasive Prediction of Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 38741808
- PMCID: PMC11090259
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.58207
Discovery and Validation of Novel microRNA Panel for Non-Invasive Prediction of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Background: Early diagnosis remains a challenge for prostate cancer (PCa) due to molecular heterogeneity. The purpose of our study was to explore the diagnostic potential of microRNA (miRNA) in both tissue and serum that may aid in the precise and early clinical diagnosis of PCa.
Materials and methods: The miRNA expression pattern analysis was carried out in 250 subjects (discovery and validation cohort). The Discovery Cohort included the control (n = 30) and PCa (n = 35) subjects, while the Validation Cohort included the healthy control (n = 60), benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) (n = 55), PCa (n = 50), and castration-resistant PCa (CRPC) (n = 20) patients. The expression analysis of tissue (Discovery Cohort) and serum (Validation Cohort) was carried out by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). The diagnostic biomarker potential was evaluated using receiver operating characteristics (ROC). Bioinformatic tools were used to explore and analyze miRNA target genes.
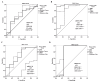
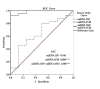
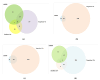
Results: MiRNA 4510 and miRNA 183 were significantly (p<0.001) upregulated and miRNA 329 was significantly (p<0.0001) downregulated in both PCa tissue and serum. ROC curve analysis showed excellent non-invasive biomarker potential of miRNA 4510 in both PCa (area under the curve (AUC) 0.984; p<0.001) and CRPC (AUC 0.944; p<0.001). The panel of serum miRNAs (miRNA 183 and miRNA 4510) designed for PCa had significant and greater AUC with both 100% sensitivity and specificity. Computational analysis shows that the maximum number of target genes are transcription factors that regulate oncogenes and tumor suppressors.
Conclusion: Based on ROC curve analysis, miRNAs 4510, 329, and 711 were identified as potential non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers in the early detection of PCa. Our findings imply that a panel of miRNAs 183 and 4510 has high specificity for distinguishing PCa from healthy controls and providing therapeutic targets for better and earlier PCa therapy.
Keywords: castration-resistant prostate cancer; diagnostic biomarker; microrna; non-invasive; panel mirna; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2024, Kumari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Comprehensive cataloging of miR-363 as a therapeutic & non-invasive biomarker of prostate cancer.Indian J Med Res. 2024 Aug;160(2):236-245. doi: 10.25259/ijmr_2274_23. Indian J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39513205 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and validation of novel serum panel of microRNA in stratification of prostate cancer.Prostate Int. 2023 Sep;11(3):150-158. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Prostate Int. 2023. PMID: 37745909 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-410-5p as a potential serum biomarker for the diagnosis of prostate cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2016 Feb 19;16:12. doi: 10.1186/s12935-016-0285-6. eCollection 2016. Cancer Cell Int. 2016. PMID: 26900347 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a three-miRNA panel in serum for bladder cancer diagnosis by a diagnostic test.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 May;11(5):1005-1016. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-2611. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35706801 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a urinary microRNA biomarker panel as a tool for early detection of prostate cancer in a Chinese population.Biomarkers. 2023 Jun;28(4):372-378. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2023.2166587. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Biomarkers. 2023. PMID: 37185057
Cited by
-
Comprehensive cataloging of miR-363 as a therapeutic & non-invasive biomarker of prostate cancer.Indian J Med Res. 2024 Aug;160(2):236-245. doi: 10.25259/ijmr_2274_23. Indian J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39513205 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Bioinformatic Analysis of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Network-Related microRNAs As Candidate Signatures in Prostate Adenocarcinoma.Cureus. 2025 Jun 20;17(6):e86467. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86467. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40693059 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-mediated resistance mechanisms in prostate cancer: implications for targeted therapy and metastatic progression.Med Oncol. 2025 Aug 29;42(10):454. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-03006-7. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40879856 Review.
References
-
- Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Serum BPSA outperforms both total PSA and free PSA as a predictor of prostatic enlargement in men without prostate cancer. Canto EI, Singh H, Shariat SF, et al. Urology. 2004;63:905–910. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
