Identification, Evaluation, and Correction of Supracrestal Tissue Attachment (Previously Biologic Width) Violation: A Case Presentation With Literature Review
- PMID: 38741844
- PMCID: PMC11089581
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.58128
Identification, Evaluation, and Correction of Supracrestal Tissue Attachment (Previously Biologic Width) Violation: A Case Presentation With Literature Review
Abstract
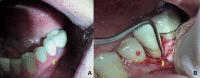
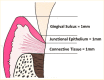
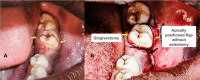
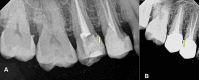
The supracrestal tissue attachment (SCTA) is the new terminology for biologic width. SCTA is defined as the physiologic dimension of a solitary functional unit composed of junctional epithelium and connective tissue attachment. Its preservation is critical for the well-being of periodontal health. SCTA has been widely studied and scientific literature is indicative of its significance during the placement of restoration, including prosthetic crowns. This should be taken care of in cases of anterior teeth within the smile zone, where dental crowns are regularly placed subgingivally for aesthetic reasons. In addition, any violation of SCTA while restoring the dentition will present as gingival inflammation and pain, consequently, leading to failure of the clinical procedure.
Keywords: biological width; biological width violation; deep margin elevation; dental crown; ferrule; precision; rapid orthodontic extrusion; restorative margin; slow orthodontic extrusion; supra crestal fiberotomy.
Copyright © 2024, Alam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Biologic width dimensions - a systematic review. Schmidt JC, Sahrmann P, Weiger R, Schmidlin PR, Walter C. J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40:493–504. - PubMed
-
- Observation and determination of periodontal tissue profile using optical coherence tomography. Kakizaki S, Aoki A, Tsubokawa M, et al. J Periodontal Res. 2018;53:188–199. - PubMed
-
- Biological width: the periodontal restorative interlink: short discussion. Almuhaiza M, Gufran K, Hamza MO. Int J Dent Med Spec. 2016;3:15.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
