The RTK-RAS signaling pathway is enriched in patients with rare acute myeloid leukemia harboring t(16;21)(p11;q22)/ FUS::ERG
- PMID: 38742238
- PMCID: PMC11090622
- DOI: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000188
The RTK-RAS signaling pathway is enriched in patients with rare acute myeloid leukemia harboring t(16;21)(p11;q22)/ FUS::ERG
Abstract
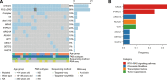
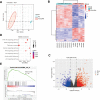
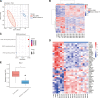
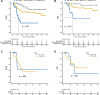
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with t(16;21)(p11;q22)/FUS::ERG is a rare AML subtype associated with poor prognosis. However, its clinical and molecular features remain poorly defined. We determined the clinicopathological, genomic, and transcriptomic characteristics and outcomes of patients with AML harboring FUS::ERG at our center. Thirty-six AML patients harboring FUS::ERG were identified, with an incidence rate of 0.3%. These patients were characterized by high lactate dehydrogenase levels (median: 838.5 U/L), elevated bone marrow blast counts (median: 71.5%), and a CD56-positive immunophenotype (94.3%). Notably, we found that RTK-RAS GTPase (RAS) pathway genes, including NRAS (33%) and PTPN11 (24%), were frequently mutated in this subtype. Transcriptome analysis revealed enrichment of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-Akt (PI3K-Akt), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and RAS signaling pathways and upregulation of BCL2, the target of venetoclax, in FUS::ERG AML compared to RUNX1::RUNX1T1 AML, a more common AML subtype with good prognosis. The median event-free survival in patients with FUS::ERG AML was 11.9 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 9.0-not available [NA]) months and the median overall survival was 18.2 (95% CI: 12.4-NA) months. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation failed to improve outcomes. Overall, the high incidence of RTK-RAS pathway mutations and high expression of BCL2 may indicate promising therapeutic targets in this high-risk AML subset.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; BCL2; RTK-RAS signaling pathway; q22)/FUS::ERG; t(16; 21)(p11.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health Inc., on behalf of the Chinese Medical Association (CMA) and Institute of Hematology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College (IHCAMS).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic impact of t(16;21)(p11;q22) and t(16;21)(q24;q22) in pediatric AML: a retrospective study by the I-BFM Study Group.Blood. 2018 Oct 11;132(15):1584-1592. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-849059. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30150206 Free PMC article.
-
[Two cases of acute myeloid leukemia with t(16;21)(p11;q22) and TLS/FUS-ERG fusion transcripts].Korean J Lab Med. 2009 Oct;29(5):390-5. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.5.390. Korean J Lab Med. 2009. PMID: 19893346 Korean.
-
Salvage therapy with azacitidine for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with t(16;21)(p11;q22)/FUS-ERG and early relapse after allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation: A case report.Clin Case Rep. 2019 Sep 27;7(11):2149-2152. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2461. eCollection 2019 Nov. Clin Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31788268 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical characteristics of acute myeloid leukemia with t (16;21) (p11;q22):nine cases report and literature review].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Mar;37(3):210-5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2016.03.007. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27033758 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
TLS/FUS-ERG fusion gene in acute leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome evolved to acute leukemia: report of six cases and a literature review.Ann Hematol. 2022 Dec;101(12):2583-2600. doi: 10.1007/s00277-022-04979-5. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Ann Hematol. 2022. PMID: 36181538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rat Sarcoma Virus Family Genes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Pathogenetic and Clinical Implications.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 15;13(1):202. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010202. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A structure-based modelling approach identifies effective drug combinations for RAS-mutant acute myeloid leukemia.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 3:2025.04.29.651188. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.29.651188. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654850 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Pan J, Zhang Y, Zhao YL, et al. . Impact of clinical factors on outcome of leukemia patients with TLS-ERG fusion gene. Leuk Lymphoma 2017;58(7):1655–1663. doi:10.1080/10428194.2016.1260124. - PubMed
-
- Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, et al. . Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022;140(12):1345–1377. doi:10.1182/blood.2022016867. - PubMed
-
- Buteyn NJ, Burke CG, Smith JL, et al. . EZH2-mediated MHC class II silencing drives immune evasion in AML with t(16;21) (FUS-ERG). Blood 2021;138(Suppl 1):374–374. doi:10.1182/blood-2021-153256.
-
- Qin YZ, Chen Y, Xu LP, et al. . Outcome and minimal residual disease monitoring in patients with t(16;21) acute myelogenous leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2018;24(1):163–168. doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.09.002. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
