OpenFold: retraining AlphaFold2 yields new insights into its learning mechanisms and capacity for generalization
- PMID: 38744917
- PMCID: PMC11645889
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-024-02272-z
OpenFold: retraining AlphaFold2 yields new insights into its learning mechanisms and capacity for generalization
Abstract
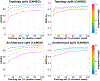
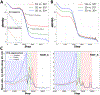
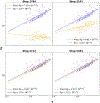
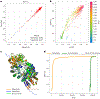
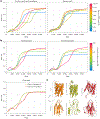
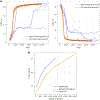
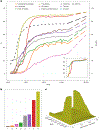
AlphaFold2 revolutionized structural biology with the ability to predict protein structures with exceptionally high accuracy. Its implementation, however, lacks the code and data required to train new models. These are necessary to (1) tackle new tasks, like protein-ligand complex structure prediction, (2) investigate the process by which the model learns and (3) assess the model's capacity to generalize to unseen regions of fold space. Here we report OpenFold, a fast, memory efficient and trainable implementation of AlphaFold2. We train OpenFold from scratch, matching the accuracy of AlphaFold2. Having established parity, we find that OpenFold is remarkably robust at generalizing even when the size and diversity of its training set is deliberately limited, including near-complete elisions of classes of secondary structure elements. By analyzing intermediate structures produced during training, we also gain insights into the hierarchical manner in which OpenFold learns to fold. In sum, our studies demonstrate the power and utility of OpenFold, which we believe will prove to be a crucial resource for the protein modeling community.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures
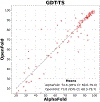
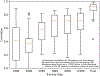
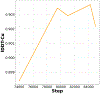
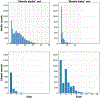
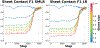
References
-
- Anfinsen CB Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science 181, 223–230 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Golkov V et al. Protein contact prediction from amino acid co-evolution using convolutional networks for graph-valued images. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (eds Lee D et al.) (Curran Associates, 2016).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 CA225088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54-CA225088/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- OAC-2106661/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- R35GM150546/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- OAC-2112606/National Science Foundation (NSF)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

