Risk factors for hemorrhagic cystitis in children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38745164
- PMCID: PMC11092211
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-024-04815-x
Risk factors for hemorrhagic cystitis in children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The risk factors for hemorrhagic cystitis (HC) in children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) are unclear. Therefore, we conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the risk factors for HC in children undergoing HSCT.
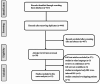
Methods: We performed this meta-analysis by retrieving studies from PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library up to October 10, 2023, and analyzing those that met the inclusion criteria. I2 statistics were used to evaluate heterogeneity.
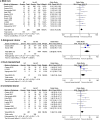
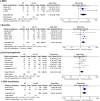
Results: Twelve studies, including 2,764 patients, were analyzed. Male sex (odds ratio [OR] = 1.52; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.16-2.00; p = 0.003, I2 = 0%), allogeneic donor (OR = 5.28; 95% CI, 2.60-10.74; p < 0.00001, I2 = 0%), human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatched donor (OR = 1.86; 95% CI, 1.00-3.44; p = 0.05, I2 = 31%), unrelated donor (OR = 1.58; 95% CI, 1.10-2.28; p = 0.01, I2 = 1%), myeloablative conditioning (MAC) (OR = 3.17; 95% CI, 1.26-7.97; p = 0.01, I2 = 0%), busulfan (OR = 2.18; 95% CI, 1.33-3.58; p = 0.002, I2 = 0%) or anti-thymoglobulin (OR = 1.65; 95% CI, 1.07-2.54; p = 0.02, I2 = 16%) use, and cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation (OR = 2.64; 95% CI, 1.44-4.82; p = 0.002, I2 = 0%) were risk factors for HC in children undergoing HSCT.
Conclusions: Male sex, allogeneic donor, HLA-mismatched, unrelated donor, MAC, use of busulfan or anti-thymoglobulin, and CMV reactivation are risk factors for HC in children undergoing HSCT.
Keywords: Children; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Hemorrhagic cystitis; Risk factors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang XH, Chen J, Han MZ, Huang H, Jiang EL, Jiang M, et al. The consensus from the Chinese Society of Hematology on indications, conditioning regimens and donor selection for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: 2021 update. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:145. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01159-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li B, Meng L, Tian Y, Lu Q, Gao L, Xiao P, et al. Outcomes and risk factors of hemorrhagic cystitis in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients using different graft source and condition with severe aplastic anemia. Hematology. 2022;27:714–22. doi: 10.1080/16078454.2022.2078538. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

