Rituximab retention rate in systemic sclerosis: a long term real-life multicentre study
- PMID: 38745439
- PMCID: PMC11879284
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae280
Rituximab retention rate in systemic sclerosis: a long term real-life multicentre study
Abstract
Objectives: To report real-life data on rituximab retention rate as an indicator of safety and efficacy in a multicentric national cohort of systemic sclerosis patients.
Methods: SSc patients treated with rituximab and followed for at least 36 months were included, clinically characterized and longitudinally monitored. A competing risk analysis with sub-hazard ratio (sHR) definition was performed to explore the clinical variables linked to specific cause of rituximab discontinuation.
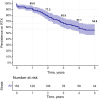
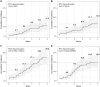
Results: One-hundred and fifty-two SSc-patients [mean age 47.3 (12.3) years; females 79.6%; diffuse disease 77.6%; anti-topoisomerase-I positivity 63.2%] were evaluated over a median (interquartile range) time of 3.3 (1.7-5.0) years. The primary indications for rituximab were interstitial lung disease (38.8%), worsening skin fibrosis (36.8%) and arthritis (13.8%); 138 patients (90.8%) received more than one rituximab course. The 5-year rituximab retention rate was 59.9% (44.6-64.7%). Clinical response was the most common reason for rituximab discontinuation [5.7; 95% CI: (3.7-8.4) per 100 patient-years] and was associated with a shorter disease duration (sHR 0.8; 95% CI: 0.7, 0.9), anti-topoisomerase-I negativity (sHR 0.4; 95% CI: 0.2, 0.9), previous digital ulcers (sHR 2.6; 95% CI: 1.1, 6.2) and no history of arthritis (sHR 0.3; 95% CI: 0.1, 0.8). Treatment failure was the second cause of rituximab discontinuation [3.7 (95% CI: 2.2, 6.0) per 100 patient-years] and was associated with anti-centromere antibody positivity (sHR 2.8; 95% CI: 1.1, 7.4) and anti-topoisomerase-I negativity (sHR 0.2; 95% CI: 0.1, 0.6). Adverse events (AEs) were the less common cause of discontinuation [3.1 (95% CI: 1.7, 5.2) per 100 patient-years], associated with limited cutaneous subset (sHR 3.4; 95% CI: 1.2, 9.7) and previous mycophenolate mofetil treatment (sHR 4.5; 95% CI: 1.2, 16.3).
Conclusion: Rituximab is a safe and effective treatment in SSc: clinical response emerged as the primary reason for rituximab discontinuation, and AEs had a limited impact on treatment persistence. The identification of specific disease features associated with a response to rituximab will be useful in the management of SSc-patients.
Keywords: B-cells; real-life data; retention rate; rituximab; systemic sclerosis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Denton CP, Khanna D.. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017;390:1685–99. - PubMed
-
- Varga J, Trojanowska M, Kuwana M.. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: recent insights of molecular and cellular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Scleroderma Relat Disord 2017;2:137–52.
-
- Distler O, Highland KB, Gahlemann M. et al.; SENSCIS Trial Investigators. Nintedanib for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med 2019;380:2518–28. - PubMed
-
- Daoussis D, Melissaropoulos K, Sakellaropoulos G. et al. A multicenter, open-label, comparative study of B-cell depletion therapy with Rituximab for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2017;46:625–31. - PubMed
-
- Bosello SL, De Luca G, Rucco M. et al. Long-term efficacy of B cell depletion therapy on lung and skin involvement in diffuse systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2015;44:428–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

