PD-L1 targeted peptide demonstrates potent antitumor and immunomodulatory activity in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 38745661
- PMCID: PMC11091243
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1367040
PD-L1 targeted peptide demonstrates potent antitumor and immunomodulatory activity in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: In recent years, immunotherapy has been emerging as a promising alternative therapeutic method for cancer patients, offering potential benefits. The expression of PD-L1 by tumors can inhibit the T-cell response to the tumor and allow the tumor to evade immune surveillance. To address this issue, cancer immunotherapy has shown promise in disrupting the interaction between PD-L1 and its ligand PD-1.
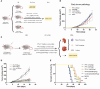
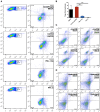
Methods: We used mirror-image phage display technology in our experiment to screen and determine PD-L1 specific affinity peptides (PPL-C). Using CT26 cells, we established a transplanted mouse tumor model to evaluate the inhibitory effects of PPL-C on tumor growth in vivo. We also demonstrated that PPL-C inhibited the differentiation of T regulatory cells (Tregs) and regulated the production of cytokines.
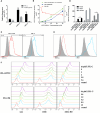
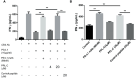
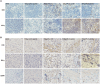
Results: In vitro, PPL-C has a strong affinity for PD-L1, with a binding rate of 0.75 μM. An activation assay using T cells and mixed lymphocytes demonstrated that PPL-C inhibits the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1. PPL-C or an anti-PD-L1 antibody significantly reduced the rate of tumor mass development in mice compared to those given a control peptide (78% versus 77%, respectively). The results of this study demonstrate that PPL-C prevents or retards tumor growth. Further, immunotherapy with PPL-C enhances lymphocyte cytotoxicity and promotes proliferation in CT26-bearing mice.
Conclusion: PPL-C exhibited antitumor and immunoregulatory properties in the colon cancer. Therefore, PPL-C peptides of low molecular weight could serve as effective cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: PD-L1 binding peptide; PPL-C; colon cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2024 Liang, Luo, Li, Liu, Habib, Liu, Huang, Wang, Yi, Hu, Zheng, Xie and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

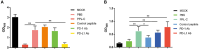

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

