Immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody/tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without transarterial chemoembolization as first-line treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CHANCE2201): a target trial emulation study
- PMID: 38745965
- PMCID: PMC11090892
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102622
Immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody/tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without transarterial chemoembolization as first-line treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CHANCE2201): a target trial emulation study
Abstract
Background: The role of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is unconfirmed. This study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) plus anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) antibody/tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) with or without TACE as first-line treatment for advanced HCC.
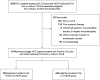
Methods: This nationwide, multicenter, retrospective cohort study included advanced HCC patients receiving either TACE with ICIs plus anti-VEGF antibody/TKIs (TACE-ICI-VEGF) or only ICIs plus anti-VEGF antibody/TKIs (ICI-VEGF) from January 2018 to December 2022. The study design followed the target trial emulation framework with stabilized inverse probability of treatment weighting (sIPTW) to minimize biases. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS). Secondary outcomes included progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and safety. The study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT05332821.
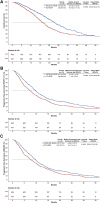
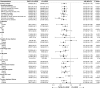
Findings: Among 1244 patients included in the analysis, 802 (64.5%) patients received TACE-ICI-VEGF treatment, and 442 (35.5%) patients received ICI-VEGF treatment. The median follow-up time was 21.1 months and 20.6 months, respectively. Post-application of sIPTW, baseline characteristics were well-balanced between the two groups. TACE-ICI-VEGF group exhibited a significantly improved median OS (22.6 months [95% CI: 21.2-23.9] vs 15.9 months [14.9-17.8]; P < 0.0001; adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.63 [95% CI: 0.53-0.75]). Median PFS was also longer in TACE-ICI-VEGF group (9.9 months [9.1-10.6] vs 7.4 months [6.7-8.5]; P < 0.0001; aHR 0.74 [0.65-0.85]) per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours (RECIST) version 1.1. A higher ORR was observed in TACE-ICI-VEGF group, by either RECIST v1.1 or modified RECIST (41.2% vs 22.9%, P < 0.0001; 47.3% vs 29.7%, P < 0.0001). Grade ≥3 adverse events occurred in 178 patients (22.2%) in TACE-ICI-VEGF group and 80 patients (18.1%) in ICI-VEGF group.
Interpretation: This multicenter study supports the use of TACE combined with ICIs and anti-VEGF antibody/TKIs as first-line treatment for advanced HCC, demonstrating an acceptable safety profile.
Funding: National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research and Development Program of China, Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Center, Collaborative Innovation Center of Radiation Medicine of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and Nanjing Life Health Science and Technology Project.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Target trial emulation; Transarterial chemoembolization; Tyrosine kinase inhibitors; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Llovet J.M., De Baere T., Kulik L., et al. Locoregional therapies in the era of molecular and immune treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(5):293–313. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

