This is a preprint.
Molecular basis for plasma membrane recruitment of PI4KA by EFR3
- PMID: 38746453
- PMCID: PMC11092606
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.30.587787
Molecular basis for plasma membrane recruitment of PI4KA by EFR3
Update in
-
Molecular basis for plasma membrane recruitment of PI4KA by EFR3.Sci Adv. 2024 Dec 20;10(51):eadp6660. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp6660. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39705356 Free PMC article.
Abstract
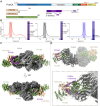
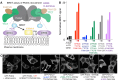
The lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol 4 kinase III alpha (PI4KIIIa/PI4KA) is a master regulator of the lipid composition and asymmetry of the plasma membrane. PI4KA exists primarily in a heterotrimeric complex with its regulatory proteins TTC7 and FAM126. Fundamental to PI4KA activity is its targeted recruitment to the plasma membrane by the lipidated proteins EFR3A and EFR3B. Here, we report a cryo-EM structure of the C-terminus of EFR3A bound to the PI4KA-TTC7B-FAM126A complex, with extensive validation using both hydrogen deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS), and mutational analysis. The EFR3A C-terminus undergoes a disorder-order transition upon binding to the PI4KA complex, with an unexpected direct interaction with both TTC7B and FAM126A. Complex disrupting mutations in TTC7B, FAM126A, and EFR3 decrease PI4KA recruitment to the plasma membrane. Multiple post-translational modifications and disease linked mutations map to this site, providing insight into how PI4KA membrane recruitment can be regulated and disrupted in human disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests J.E.B. reports personal fees from Scorpion Therapeutics and Reactive therapeutics; and research contracts from Novartis and Calico Life Sciences.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
