Nursing staff involvement of children in care activities: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38746576
- PMCID: PMC11080329
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2023.100160
Nursing staff involvement of children in care activities: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Nurses' involvement of children in their care is essential to quality pediatric care. Various international guidelines stress the need for children's involvement in decisions and activities affecting their care and lives; widely known among them is the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child. This convention gives children the right to participate in decisions and activities that affect their growth and development.
Objective: This study assessed the level of nursing staff involvement of children in care activities and the benefits they perceived from this involvement.
Design: Descriptive cross-sectional study.
Setting: Units of Evangelical Church of Ghana Hospital, Kpandai rendering services for children.
Participants: A total of 116 nursing staff members were invited to participate; 97 (84%) responded. The term "nurses" in this study includes unlicensed nursing assistants, as well as licensed professional nursing staff.
Methods: Descriptive statistics were used to analyze participants' demographic characteristics and the nurses' perceived benefits derived from children's involvement in care activities. A Chi-square test was used to analyze associations between nurses' demographic data and the level of nurses' involvement of children in care activities at a significance level of p< 0.05.
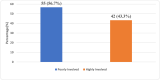
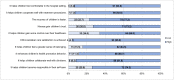
Results: A majority (56.7%) of the nurses poorly involved children in their care activities. They either involved children to some extent or did not involve children at all. Nurses' age and gender predicted involvement. Older nurses aged 30 and above (56.4%) were more likely to involve children in care activities than those under 30 (26.1%) [p=0.003]. Female nurses (31.7%) were marginally less likely to involve children in their care activities than their male colleagues (51.8%) [p=0.049]. Most of the nurses agreed to several impactful benefits of involving children in care activities, thus benefiting children, caregivers, and health professionals.
Conclusion: The overall level of nurses' involvement of children in care activities was poor. Policy documents to safeguard children's rights in healthcare involvement must be developed and implemented from the national down to the hospital level to safeguard children's rights to healthcare involvement.
Keywords: Children; Children involvement; Children's rights; Children's rights in Ghana; Nursing care involvement; Patient participation; Pediatric Care.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest exists, according to the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Adonteng-kissi O. Child labour versus realising children's right to provision, protection, and participation in Ghana. Aust. Soc. Work. 2021;74(4):464–479. doi: 10.1080/0312407X.2020.1742363. - DOI
-
- Aston H.J., Lambert N. Young people's views about their involvement in decision-making. Educ. Psychol. Pract. 2010;26(1):41–51. doi: 10.1080/02667360903522777. - DOI
-
- Bäckström K. Convention on the rights of the child. Int. J. Early Childhood. 1989;21(2):35–44. doi: 10.1007/BF03174582. - DOI
-
- Berg S.K., Færch J., Cromhout P.F., Tewes M., Pedersen P.U., Rasmussen T.B., Missel M., Christensen J., Juel K., Christensen A.V. Questionnaire measuring patient participation in health care: scale development and psychometric evaluation. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2020;19(7):600–608. doi: 10.1177/1474515120913809. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources