Fusion rate and complications of oblique lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 38746621
- PMCID: PMC11091322
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1374134
Fusion rate and complications of oblique lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: There currently exists some controversy about the efficacy of oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases.
Aim: This study compares the application effects of OLIF and TLIF in lumbar degenerative diseases by reviewing the literature and using meta-analysis.
Methods: We included randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing TLIF and OLIF in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases. We searched for words such as "intervertebral disc degeneration," "spinal fusion," and "lumbar vertebrae" in the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases. The search date was set from the establishment date of the database to October 2023. Two authors independently conducted document screening, data abstraction, and qualitative assessment. A meta-analysis was performed and adapted to RevMan5.3 software. The odds ratio (OR), weighted mean difference (WMD), and 95% CI were calculated by adopting a fixed-effect model (FEM) or a random-effect model (REM).
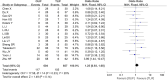
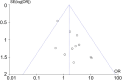
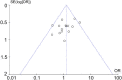
Results: A total of 18 cohort studies were included with 1,550 patients, of whom 806 patients underwent TLIF (TLIF group) and 744 patients underwent OLIF (OLIF group). There were no significant differences found in the fusion rate [OR = 1.58 (0.95, 2.64), P = 0.08], complication rate [OR = 1.25 (0.93, 1.68), P = 0.14], and visual analog scale for back pain (VAS-BP) [WMD = 0.00 (-0.13, 0.14), P = 0.96] between the two groups. Compared with the TLIF group, the OLIF group had a lower Oswestry disability index (ODI) [WMD = -0.62 (-1.03, -0.20), P = 0.003], a higher foramen height (FH) [WMD = 2.03 (1.42, 2.46), P < 0.001], a higher disc height (DH) [WMD = 1.69 (1.17, 2.22), P < 0.001], and a shorter length of stay (LOS) [WMD = -1.80 (-2.55, -1.05), P < 0.001].
Conclusion: In the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases, compared with TLIF, OLIF has more advantages in terms of improving the lumbar function, restoring the FH and DH, and shortening the LOS. Both methods have comparable fusion rates, complication rates, and lumbar pain improvements. Due to the small amount of research and unclear assessment of the risk of bias, high-quality, large-sample randomized controlled studies are required to prove it.
Keywords: OLIF; TLIF; complication rate; fusion rate; lumbar degenerative disease; meta-analysis.
© 2024 Xiao, Duan, Pan and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus oblique lumbar interbody fusion for treating lumbar degenerative diseases.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Dec 30;19(1):891. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05422-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39736715 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of clinical effect and muscle injury imaging between oblique lateral lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of single-segment degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023 May 25;36(5):420-7. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2023.05.005. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023. PMID: 37211932 Chinese.
-
Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus oblique lateral interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative disease: a meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Sep 18;22(1):802. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04687-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34537023 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of oblique lumbar interbody fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Sep;143(9):5657-5670. doi: 10.1007/s00402-023-04880-4. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 37079105 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the medium-term outcomes of lumbar interbody fusion via transforaminal and oblique approach in treating lumbar degenerative disc diseases.Spine J. 2022 Jun;22(6):993-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2021.12.006. Epub 2021 Dec 11. Spine J. 2022. PMID: 34906739
Cited by
-
Advantages of a new improved oblique Retractor in oblique lateral lumbar interbody fusion: a retrospective study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jun 10;20(1):581. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05992-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40495186 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

