Clinical research nursing pathways: The development and evaluation of a nursing research internship program using the RE-AIM framework
- PMID: 38746823
- PMCID: PMC11080478
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2024.100176
Clinical research nursing pathways: The development and evaluation of a nursing research internship program using the RE-AIM framework
Abstract
Background: In 2018 a Nursing Research Internship program was started within a major referral and tertiary teaching centre in Australia.
Aim: We aimed to evaluate the first 12 months of the program using an implementation science framework.
Methods: This was a qualitative study. Following ethical approval n = 20 semi -structured interviews were recorded and transcribed verbatim. Participants included nurses with clinical, research and management roles who had engaged in or supported a Nursing Research Internship program. The Framework Method was conducted to analyse the findings.
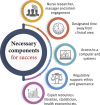
Results: Key themes identified included 'What is the impact of a Nursing Research Internship program?'; 'Why do a Nursing Research Internship program?'; 'How do we do a Nursing Research Internship program?'; 'How do we sustain a Nursing Research Internship program?'. Positive impacts were identified for clinical nurses and their teams, for the hospital and health service, and for patients and families. Identified key components included protected research time, specialist support (including library, statistics, health economist, implementation scientist), regulatory support (ethics and governance procedures) and access to a computer and IT resources. The Nursing Research Internship program required support from nurse clinicians, nurse managers and nurse academics.
Conclusion: A structured Nursing Research Internship program supports clinical nurses to answer research questions identified directly from clinical practice.
Keywords: Clinician researcher; Evidence based practice; Implementation science; Nursing; RE-AIM; Research qualitative researcher.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Australian Clinical Trials Alliance and Quantium Health Outcomes . Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care; 2017. Economic Evaluation of Investigator-Initiated Clinical Trials Conducted By Networks. Sydney, Australia.
-
- Baltruks D., Callaghan P. Council of Deans of Health; 2018. Nursing, Midwifery and Allied Health Clinical Academic Research Careers in the UK. London.
-
- Black A.T., Ali S., Baumbush J., McNamee K., Mackay M. Practice-based nursing research: evaluation of clinical and professional impacts from a research training programme. J. Clin. Nurs. 2019;28(13–14):2681–2687. - PubMed
-
- Blevins S., Millen E. Foundation for new graduate nurse success. Medsurg Nurs.Off. J. Acad. Med. Surgical Nurses. 2016;25:194–195. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources