Iodine-promoted amide formation via oxidative cleavage of indoles: novel quinazoline-4(3 H)-one and tryptanthrin syntheses
- PMID: 38746844
- PMCID: PMC11091796
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra01807a
Iodine-promoted amide formation via oxidative cleavage of indoles: novel quinazoline-4(3 H)-one and tryptanthrin syntheses
Abstract
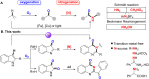
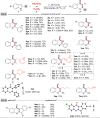
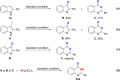
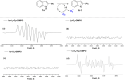
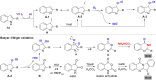
A highly efficient method for the direct construction of amide bonds via a selective cleavage of C-H and C[double bond, length as m-dash]C bonds in indole structures using an iodine-promoted approach was developed. Mechanistic studies indicated the formation of superoxide radicals obtained from molecular oxygen activation as a key intermediate step, which provided a precursor for subsequent oxidative ring-opening and intermolecular cyclization. A broad range of quinazolin-4(3H)-ones and tryptanthrins were synthesized in moderate to good yields under mild and environmentally benign conditions.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Oremland R. S. Culbertson C. W. Nature. 1992;356:421–423.
- Holmes A. J. Costello A. Lidstrom M. E. Murrell J. C. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995;132:203–208. - PubMed
- Holmes A. J. Roslev P. McDonald I. R. Iversen N. Henriksen K. Murrell J. C. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999;65:3312–3318. - PMC - PubMed
- Ma Q. Zhang X. Qu Y. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:2625. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaur K. Srivastava S. New J. Chem. 2020;44:18530–18572.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

