Imaging in the diagnosis and management of fibrosing interstitial lung diseases
- PMID: 38746908
- PMCID: PMC11091715
- DOI: 10.1183/20734735.0006-2024
Imaging in the diagnosis and management of fibrosing interstitial lung diseases
Abstract
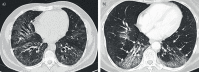
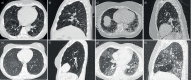
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis and management of interstitial lung diseases (ILDs), particularly given the approval of antifibrotic agents for conditions like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Diagnosing fibrotic pulmonary disorders through HRCT involves a detailed and methodical examination. The identification of specific lung tissue changes, including ground-glass opacities and reticulation, along with signs of fibrosis like honeycombing, traction bronchiectasis and lung volume loss, establishes clear HRCT patterns indicative of various ILDs. The reliability of these patterns in predicting pathological conditions depends largely on the clinical context. For instance, when a usual interstitial pneumonia pattern is present, the predictive value of this diagnosis is so high that a lung biopsy is considered to be redundant. This review intends to delineate the HRCT signs of fibrosis, elucidate the specific radiological patterns of fibrotic lung diseases, and identify the clinical circumstances under which these patterns emerge. Additionally, we introduce and discuss novel imaging techniques that hold promise for the diagnosis, screening and early detection of ILDs.
Copyright ©ERS 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M. Storman and C. Lederer have no conflicts of interests that relate to this article. D.L. Tarnoki and A.D. Tarnoki declare they have received funding outside the present work from the Bólyai scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, from ÚNKP-20-5 and ÚNKP-21-5 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology from the source of the National Research, Development, and Innovation Fund, and from the Hungarian National Laboratory (under the National Tumor Biology Laboratory project, NLP-17). G.A. Margaritopoulos has received speaking fees from Boehringer Ingelheim. H. Prosch has received speaking fees from AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Siemens and Takeda, and has received research support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Siemens and the EU Commission (EU4Health, Horizon Europe Health).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical diagnosis of patients subjected to surgical lung biopsy with a probable usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on high-resolution computed tomography.BMC Pulm Med. 2020 Nov 16;20(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-01339-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 33198708 Free PMC article.
-
"Velcro-type" crackles predict specific radiologic features of fibrotic interstitial lung disease.BMC Pulm Med. 2018 Jun 18;18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0670-0. BMC Pulm Med. 2018. PMID: 29914454 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of chest HRCT in the diagnostic evaluation of fibrosing interstitial lung diseases.J Bras Pneumol. 2021 May 31;47(3):e20200096. doi: 10.36416/1806-3756/e20200096. eCollection 2021. J Bras Pneumol. 2021. PMID: 34076172 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Current Perspective.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 16;9(9):1237. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091237. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and Radiological Features of Interstitial Lung Diseases Associated with Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Nov 30;58(12):1757. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121757. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36556960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung diseases : A pattern-based approach to diagnosis].Radiologie (Heidelb). 2025 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s00117-025-01492-4. Online ahead of print. Radiologie (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40844523 Review. German.
-
Assessing the global burden of interstitial lung disease and pulmonary sarcoidosis using multiple statistical models: analysis and future projections.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Jul 24;25(1):352. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03813-8. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40707937 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Hemogram-Derived Ratios and Liver Fibrosis Scores in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Oct 16;60(10):1702. doi: 10.3390/medicina60101702. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39459489 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of slice thickness on quantitative analysis of interstitial lung disease: a retrospective volumetric chest CT study.Radiol Med. 2025 Aug;130(8):1172-1182. doi: 10.1007/s11547-025-02023-w. Epub 2025 May 27. Radiol Med. 2025. PMID: 40423769 Free PMC article.
-
Lung ultrasound for assessing disease progression in UIP and NSIP: a comparative study with HRCT and PFT/DLCO.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Jan 9;25(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03433-8. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 39789530 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
