Leaflet modification before transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients at risk for coronary obstruction: the ShortCut study
- PMID: 38747561
- PMCID: PMC11365606
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae303
Leaflet modification before transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients at risk for coronary obstruction: the ShortCut study
Abstract
Background and aims: This trial sought to assess the safety and efficacy of ShortCut, the first dedicated leaflet modification device, prior to transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) in patients at risk for coronary artery obstruction.
Methods: This pivotal prospective study enrolled patients with failed bioprosthetic aortic valves scheduled to undergo TAVI and were at risk for coronary artery obstruction. The primary safety endpoint was procedure-related mortality or stroke at discharge or 7 days, and the primary efficacy endpoint was per-patient leaflet splitting success. Independent angiographic, echocardiographic, and computed tomography core laboratories assessed all images. Safety events were adjudicated by a clinical events committee and data safety monitoring board.
Results: Sixty eligible patients were treated (77.0 ± 9.6 years, 70% female, 96.7% failed surgical bioprosthetic valves, 63.3% single splitting and 36.7% dual splitting) at 22 clinical sites. Successful leaflet splitting was achieved in all [100%; 95% confidence interval (CI) 94%-100.0%, P < .001] patients. Procedure time, including imaging confirmation of leaflet splitting, was 30.6 ± 17.9 min. Freedom from the primary safety endpoint was achieved in 59 [98.3%; 95% CI (91.1%-100%)] patients, with no mortality and one (1.7%) disabling stroke. At 30 days, freedom from coronary obstruction was 95% (95% CI 86.1%-99.0%). Within 90 days, freedom from mortality was 95% [95% CI (86.1%-99.0%)], without any cardiovascular deaths.
Conclusions: Modification of failed bioprosthetic aortic valve leaflets using ShortCut was safe, achieved successful leaflet splitting in all patients, and was associated with favourable clinical outcomes in patients at risk for coronary obstruction undergoing TAVI.
Keywords: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation; Valve Academic Research Consortium; Valve in valve; Virtual transcatheter heart valve to coronary artery; Virtual transcatheter heart valve to sinotubular junction.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


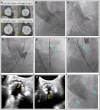
References
-
- Dvir D, Leipsic J, Blanke P, Ribeiro HB, Kornowski R, Pichard A, et al. . Coronary obstruction in transcatheter aortic valve-in-valve implantation: preprocedural evaluation, device selection, protection, and treatment. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2015;8:e002079. 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.114.002079 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blanke P, Soon J, Dvir D, Park JK, Naoum C, Kueh SH, et al. . Computed tomography assessment for transcatheter aortic valve in valve implantation: the Vancouver approach to predict anatomical risk for coronary obstruction and other considerations. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 2016;10:491–9. 10.1016/j.jcct.2016.09.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro HB, Rodes-Cabau J, Blanke P, Leipsic J, Kwan Park J, Bapat V, et al. . Incidence, predictors, and clinical outcomes of coronary obstruction following transcatheter aortic valve replacement for degenerative bioprosthetic surgical valves: insights from the VIVID registry. Eur Heart J 2018;39:687–95. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx455 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

