1H/17O Chemical Shift Waves in Carboxyl-Bridged Hydrogen Bond Networks in Organic Solids
- PMID: 38748612
- PMCID: PMC11840671
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.4c01866
1H/17O Chemical Shift Waves in Carboxyl-Bridged Hydrogen Bond Networks in Organic Solids
Abstract
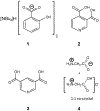
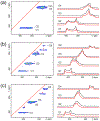
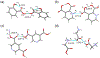
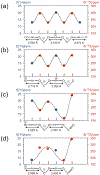
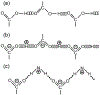
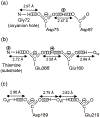
We report solid-state 1H and 17O NMR results for four 17O-labeled organic compounds each containing an extensive carboxyl-bridged hydrogen bond (CBHB) network in the crystal lattice: tetrabutylammonium hydrogen di-[17O2]salicylate (1), [17O4]quinolinic acid (2), [17O4]dinicotinic acid (3), and [17O2]Gly/[17O2]Gly·HCl cocrystal (4). The 1H isotropic chemical shifts found for protons involved in different CBHB networks are between 8.2 and 20.5 ppm, which reflect very different hydrogen-bonding environments. Similarly, the 17O isotropic chemical shifts found for the carboxylate oxygen atoms in CBHB networks, spanning a large range between 166 and 341 ppm, are also remarkably sensitive to the hydrogen-bonding environments. We introduced a simple graphical representation in which 1H and 17O chemical shifts are displayed along the H and O atomic chains that form the CBHB network. In such a depiction, because wavy patterns are often observed, we refer to these wavy patterns as 1H/17O chemical shift waves. Typical patterns of 1H/17O chemical shift waves in CBHB networks are discussed. The reported 1H and 17O NMR parameters for the CBHB network models examined in this study can serve as benchmarks to aid in spectral interpretation for CBHB networks in proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Huggins ML Hydron bridges in organic compounds. J. Org. Chem 1936, 1, 407–456.
-
- Hendricks SB The orientation of the oxalate group in oxalic acid and some of its salts. Z. Kristallogr 1935, 91, 48–64.
-
- Derissen JL; Smith PH Refinement of the crystal structures of anhydrous [alpha]- and [beta]-oxalic acids. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B 1974, 30, 2240–2242.
-
- Leiserowitz L Molecular packing modes. Carboxylic acids. Acta Cryst. 1976, B32, 775–802.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

