An age-progressive platelet differentiation path from hematopoietic stem cells causes exacerbated thrombosis
- PMID: 38749423
- PMCID: PMC12047039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.04.018
An age-progressive platelet differentiation path from hematopoietic stem cells causes exacerbated thrombosis
Abstract
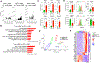
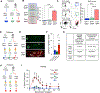
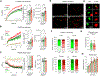
Platelet dysregulation is drastically increased with advanced age and contributes to making cardiovascular disorders the leading cause of death of elderly humans. Here, we reveal a direct differentiation pathway from hematopoietic stem cells into platelets that is progressively propagated upon aging. Remarkably, the aging-enriched platelet path is decoupled from all other hematopoietic lineages, including erythropoiesis, and operates as an additional layer in parallel with canonical platelet production. This results in two molecularly and functionally distinct populations of megakaryocyte progenitors. The age-induced megakaryocyte progenitors have a profoundly enhanced capacity to engraft, expand, restore, and reconstitute platelets in situ and upon transplantation and produce an additional platelet population in old mice. The two pools of co-existing platelets cause age-related thrombocytosis and dramatically increased thrombosis in vivo. Strikingly, aging-enriched platelets are functionally hyper-reactive compared with the canonical platelet populations. These findings reveal stem cell-based aging as a mechanism for platelet dysregulation and age-induced thrombosis.
Keywords: aging; cardiovascular disorder; genetic lineage tracing; hematopoietic stem cells; megakaryocyte progenitor cells; platelet differentiation pathway; platelet dysregulation; thrombocytosis; thrombosis; transplantation.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
A distinct platelet differentiation pathway is involved in age-related thrombocytosis.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024 Jul;21(7):438. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01043-9. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38811855 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kim S-H, Im J-A, Lee J-W, and Lee D-C (2006). Age Related Increase of Platelet Activation. Biomedical Science Letters 12, 337–341.
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Delling FN, et al. (2020). Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 141, E139–E596. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

