Clear effects on root system architecture of winter wheat cultivars (Triticum aestivum L.) from cultivation environment and practices
- PMID: 38750060
- PMCID: PMC11096180
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-61765-1
Clear effects on root system architecture of winter wheat cultivars (Triticum aestivum L.) from cultivation environment and practices
Abstract
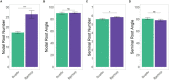
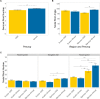
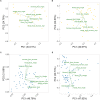
Roots play a pivotal role in the adaption of a plant to its environment, with different root traits adapting the plant to different stresses. The environment affects the Root System Architecture (RSA), but the genetic factors determine to what extent, and whether stress brought about by extreme environmental conditions is detrimental to a specific crop. This study aimed to identify differences in winter wheat RSA caused by cultivation region and practice, in the form of preceding crop (precrop), and to identify if modern cultivars used in Sweden differ in their reaction to these environments. This was undertaken using high-throughput phenotyping to assess the RSA. Clear differences in the RSA were observed between the Swedish cultivation regions, precrop treatments, and interaction of these conditions with each other and the genetics. Julius showed a large difference between cultivars, with 9.3-17.1% fewer and 12-20% narrower seminal roots. Standardized yield decreased when grown after wheat, 23% less compared to oilseed rape (OSR), and when grown in the Southern region, 14% less than the Central region. Additionally, correlations were shown between the root number, angle, and grain yield, with different root types being correlated depending on the precrop. Cultivars on the Swedish market show differences that can be adapted to the region-precrop combinations. The differences in precrop effect on RSA between regions show global implications and a need for further assessment. Correlations between RSA and yield, based on root-type × precrop, indicate different needs of the RSA depending on the management practices and show the potential for improving crop yield through targeting genotypic and environmental conditions in a holistic manner. Understanding this RSA variance, and the mechanisms of conditional response, will allow targeted cultivar breeding for specific environments, increasing plant health and food security.
Keywords: Triticum aestivum; Precrop effect; Root growth; Root system architecture; Wheat yield.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Precrop-treated soil influences wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root system architecture and its response to drought.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jun 4;15:1389593. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1389593. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38895614 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying seedling root architectural traits associated with yield and yield components in wheat.Ann Bot. 2017 May 1;119(7):1115-1129. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcx001. Ann Bot. 2017. PMID: 28200109 Free PMC article.
-
An automated root phenotype platform enables nondestructive high-throughput root system architecture dissection in wheat.Plant Physiol. 2025 Apr 30;198(1):kiaf154. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf154. Plant Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40305672
-
Wheat root systems as a breeding target for climate resilience.Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Jun;134(6):1645-1662. doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-03819-w. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Theor Appl Genet. 2021. PMID: 33900415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of genotype x environment interactions to understand rooting depth and the ability of wheat to penetrate hard soils.Ann Bot. 2013 Jul;112(2):359-68. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcs251. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Ann Bot. 2013. PMID: 23204508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precrop-treated soil influences wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root system architecture and its response to drought.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jun 4;15:1389593. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1389593. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38895614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Troedsson T, Wiberg M. The Royal Academy of Agricultural and Forest. Stockholm; 1986.
-
- Kanbar A, Toorchi M, Shashidhar HE. Relationship between root and yield morphological characters in rainfed low land rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cereal Res. Commun. 2009;37:261–268. doi: 10.1556/CRC.37.2009.2.14. - DOI
-
- Iqbal S, et al. Root morphological adjustments of crops to improve nutrient use efficiency in limited environments. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020;51:2452–2465. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2020.1836199. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HeRo - Healthy Roots: Development of tools for the selection of robust cultivars in Swedish plant breeding, with focus on the root system/Sweden SLU Grogrund
- HeRo - Healthy Roots: Development of tools for the selection of robust cultivars in Swedish plant breeding, with focus on the root system/Sweden SLU Grogrund
- HeRo - Healthy Roots: Development of tools for the selection of robust cultivars in Swedish plant breeding, with focus on the root system/Sweden SLU Grogrund
- HeRo - Healthy Roots: Development of tools for the selection of robust cultivars in Swedish plant breeding, with focus on the root system/Sweden SLU Grogrund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

