CCT6A facilitates lung adenocarcinoma progression and glycolysis via STAT1/HK2 axis
- PMID: 38750462
- PMCID: PMC11094951
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05284-7
CCT6A facilitates lung adenocarcinoma progression and glycolysis via STAT1/HK2 axis
Abstract
Background: Chaperonin Containing TCP1 Subunit 6 A (CCT6A) is a prominent protein involved in the folding and stabilization of newly synthesized proteins. However, its roles and underlying mechanisms in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), one of the most aggressive cancers, remain elusive.
Methods: Our study utilized in vitro cell phenotype experiments to assess CCT6A's impact on the proliferation and invasion capabilities of LUAD cell lines. To delve into CCT6A's intrinsic mechanisms affecting glycolysis and proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma, we employed transcriptomic sequencing and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and chromatin immunoprecipitation (CHIP) assays were also conducted to substantiate the mechanism.
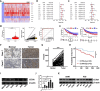
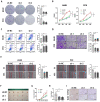
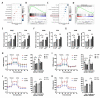
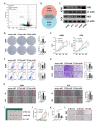
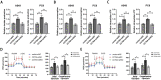
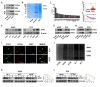
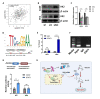
Results: CCT6A was found to be significantly overexpressed in LUAD and associated with a poorer prognosis. The silencing of CCT6A inhibited the proliferation and migration of LUAD cells and elevated apoptosis rates. Mechanistically, CCT6A interacted with STAT1 protein, forming a complex that enhances the stability of STAT1 by protecting it from ubiquitin-mediated degradation. This, in turn, facilitated the transcription of hexokinase 2 (HK2), a critical enzyme in aerobic glycolysis, thereby stimulating LUAD's aerobic glycolysis and progression.
Conclusion: Our findings reveal that the CCT6A/STAT1/HK2 axis orchestrated a reprogramming of glucose metabolism and thus promoted LUAD progression. These insights position CCT6A as a promising candidate for therapeutic intervention in LUAD treatment.
Keywords: Aerobic glycolysis; CCT6A; HK2; Lung adenocarcinoma; STAT1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HSPE1 enhances aerobic glycolysis to promote progression of lung adenocarcinoma.Mutat Res. 2024 Jul-Dec;829:111867. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2024.111867. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Mutat Res. 2024. PMID: 38878504
-
Chaperonin-containing TCP1 subunit 6A inhibition via TRIM21-mediated K48-linked ubiquitination suppresses triple-negative breast cancer progression through the AKT signalling pathway.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70097. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70097. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39556022 Free PMC article.
-
CCT6A Regulates Cervical Cancer Cell Glycolysis and Proliferation under Hypoxic Conditions via the Telomerase Cajal Body Protein 1/Telomerase Reverse Tranase.Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2025;90(1):30-41. doi: 10.1159/000539042. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2025. PMID: 38657573
-
CCT6A and CHCHD2 Are Coamplified with EGFR and Associated with the Unfavorable Clinical Outcomes of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Dis Markers. 2022 Jul 28;2022:1560199. doi: 10.1155/2022/1560199. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35937942 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor FOXA1 Facilitates Glycolysis and Proliferation of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Activation of TEX19.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;66(8):2144-2154. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00848-2. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37606876
Cited by
-
TRIM38 Suppresses the Progression of Colorectal Cancer via Enhancing CCT6A Ubiquitination to Inhibit the MYC Pathway.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(16):e2411285. doi: 10.1002/advs.202411285. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40047371 Free PMC article.
-
A method for the identification of lactate metabolism-related prognostic biomarkers and its validations in non-small cell lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 17;15(1):5812. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85620-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39962075 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the "inflammation-immunity-metabolism" network in non-small cell lung cancer: a multi-omics analysis.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 21;16(1):847. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02692-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40397292 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Antitumor Activity of Korean Black Soybean Cultivar 'Soman' by Targeting STAT-Mediated Aerobic Glycolysis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Feb 18;14(2):228. doi: 10.3390/antiox14020228. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002413 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing to identify a distinct tumor stem cells and construct a novel prognostic signature for evaluating prognosis and immunotherapy in LUAD.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 22;23(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06243-6. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39987127 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

