Clinical and genetic analysis of methylmalonic aciduria in 60 patients from Southern China: a single center retrospective study
- PMID: 38750596
- PMCID: PMC11097538
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-024-03210-0
Clinical and genetic analysis of methylmalonic aciduria in 60 patients from Southern China: a single center retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Methylmalonic aciduria (MMA) is a group of rare genetic metabolic disorders resulting from defects in methylmalonyl coenzyme A mutase (MCM) or intracellular cobalamin (cbl) metabolism. MMA patients show diverse clinical and genetic features across different subtypes and populations.
Methods: We retrospectively recruited 60 MMA patients from a single center and diagnosed them based on their clinical manifestations and biochemical assays. We then performed genetic analysis to confirm the diagnosis and identify the causal variants.
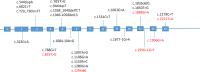
Results: We confirmed the common clinical manifestations of MMA reported previously. We also described four rare MMA cases with unusual symptoms or genetic variants, such as pulmonary hypertension or limb weakness in late-onset patients. We identified 15 MMACHC and 26 MMUT variants in 57 patients, including 6 novel MMUT variants. Two patients had only one MMAA variant each, and one patient had mild MMA due to mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome caused by a SUCLA2 variant. Among 12 critically ill patients, isolated MMA was associated with higher C3, blood ammonia, and acidosis, while combined MMA was linked to hydrocephalus on skull MRI. MMACHC c.658-660delAAG and MMUT c.1280G > A variants were correlated with more severe phenotypes.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates the clinical and genotypic heterogeneity of MMA patients and indicates that metabolic screening and genetic analysis are useful tools to identify rare cases.
Keywords: MMACHC gene; MMUT gene; Methylmalonic aciduria; Pulmonary hypertension; SUCLA2 gene.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A study on a cohort of 301 Chinese patients with isolated methylmalonic acidemia.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2020 May;43(3):409-423. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12183. Epub 2019 Nov 26. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2020. PMID: 31622506
-
Autozygosity mapping of methylmalonic acidemia associated genes by short tandem repeat markers facilitates the identification of five novel mutations in an Iranian patient cohort.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Oct;33(5):1689-1697. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0277-4. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 30022420
-
[Pulmonary arterial hypertension as leading manifestation of methylmalonic aciduria: clinical characteristics and gene testing in 15 cases].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017 Oct 18;49(5):768-777. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017. PMID: 29045954 Chinese.
-
Systematic literature review and meta-analysis on the epidemiology of methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) with a focus on MMA caused by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (mut) deficiency.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019 Apr 25;14(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13023-019-1063-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019. PMID: 31023387 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome induced by CblC subtype of methylmalonic academia: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Oct;96(43):e8284. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008284. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29068997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spectrum of genetic mutations in methylmalonic aciduria among Iranian patients.Sci Rep. 2025 May 12;15(1):16389. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01563-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40355523 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic analysis of methylmalonic aciduria in 60 patients from Southern China: a single center retrospective study.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Feb 7;20(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03585-8. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 39920767 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- A2021229/Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province of China
- 02-410-2302144XM/Plan on enhancing scientific research in GMU
- 2021A1515011312/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 202102020732/Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Project
- K-202108-5/Guangdong Medical Development Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

