Integrating clinical research into electronic health record workflows to support a learning health system
- PMID: 38751411
- PMCID: PMC11095974
- DOI: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooae023
Integrating clinical research into electronic health record workflows to support a learning health system
Abstract
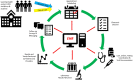
Objective: Integrating clinical research into routine clinical care workflows within electronic health record systems (EHRs) can be challenging, expensive, and labor-intensive. This case study presents a large-scale clinical research project conducted entirely within a commercial EHR during the COVID-19 pandemic.
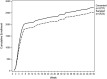
Case report: The UCSD and UCSDH COVID-19 NeutraliZing Antibody Project (ZAP) aimed to evaluate antibody levels to SARS-CoV-2 virus in a large population at an academic medical center and examine the association between antibody levels and subsequent infection diagnosis.
Results: The project rapidly and successfully enrolled and consented over 2000 participants, integrating the research trial with standing COVID-19 testing operations, staff, lab, and mobile applications. EHR-integration increased enrollment, ease of scheduling, survey distribution, and return of research results at a low cost by utilizing existing resources.
Conclusion: The case study highlights the potential benefits of EHR-integrated clinical research, expanding their reach across multiple health systems and facilitating rapid learning during a global health crisis.
Keywords: COVID-19 antibodies; EHR-integration; clinical informatics; clinical research; interoperability.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrating a Patient Engagement App into an Electronic Health Record-Enabled Workflow Using Interoperability Standards.Appl Clin Inform. 2022 Oct;13(5):1163-1171. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1758736. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Appl Clin Inform. 2022. PMID: 36516969 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Option Grid Patient Decision Aids in the Epic Electronic Health Record: Case Study at 5 Health Systems.J Med Internet Res. 2021 May 3;23(5):e22766. doi: 10.2196/22766. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33938806 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating clinical research with the Healthcare Enterprise: from the RE-USE project to the EHR4CR platform.J Biomed Inform. 2011 Dec;44 Suppl 1:S94-S102. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2011.07.007. Epub 2011 Aug 25. J Biomed Inform. 2011. PMID: 21888989
-
The Clinical Information Systems Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic.Yearb Med Inform. 2021 Aug;30(1):105-125. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1726513. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Yearb Med Inform. 2021. PMID: 34479384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Open-Source Electronic Health Record Systems for Low-Resource Settings: Systematic Review.JMIR Med Inform. 2017 Nov 13;5(4):e44. doi: 10.2196/medinform.8131. JMIR Med Inform. 2017. PMID: 29133283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antibody Levels From High-Throughput Variant-Specific SARS-CoV-2 Anti-Spike Immunoglobulin G and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Neutralization Assays Correlate With COVID-19 Infection Risk in a Large Population.J Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 15;231(4):921-930. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae622. J Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39676529
-
Longitudinal assessment of the impact of COVID-19 infection on mask-wearing behaviors.BMC Public Health. 2024 Aug 16;24(1):2230. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19776-0. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39152377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coorevits P, Sundgren M, Klein GO, et al.Electronic health records: new opportunities for clinical research. J Intern Med. 2013;274(6):547-560. - PubMed
-
- Bruland P, Doods J, Brix T, Dugas M, Storck M.. Connecting healthcare and clinical research: workflow optimizations through seamless integration of the EHR, pseudonymization services and EDC systems. Int J Med Inform. 2018;119:103-108. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
