Influence of metallic particles and TNF on the transcriptional regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome-associated genes in human osteoblasts
- PMID: 38751427
- PMCID: PMC11094288
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397432
Influence of metallic particles and TNF on the transcriptional regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome-associated genes in human osteoblasts
Abstract
Introduction: The release of mature interleukin (IL-) 1β from osteoblasts in response to danger signals is tightly regulated by the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain leucine-rich repeat and pyrin-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. These danger signals include wear products resulting from aseptic loosening of joint arthroplasty. However, inflammasome activation requires two different signals: a nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB)-activating priming signal and an actual inflammasome-activating signal. Since human osteoblasts react to wear particles via Toll-like receptors (TLR), particles may represent an inflammasome activator that can induce both signals.
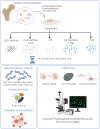
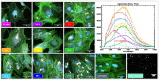
Methods: Temporal gene expression profiles of TLRs and associated intracellular signaling pathways were determined to investigate the period when human osteoblasts take up metallic wear particles after initial contact and initiate a molecular response. For this purpose, human osteoblasts were treated with metallic particles derived from cobalt-chromium alloy (CoCr), lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) alone or in combination for incubation times ranging from one hour to three days. Shortly after adding the particles, their uptake was observed by the change in cell morphology and spectral data.
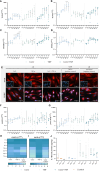
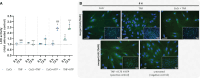
Results: Exposure of osteoblasts to particles alone increased NLRP3 inflammasome-associated genes. The response was not significantly enhanced when cells were treated with CoCr + LPS or CoCr + TNF, whereas inflammation markers were induced. Despite an increase in genes related to the NLRP3 inflammasome, the release of IL-1β was unaffected after contact with CoCr particles.
Discussion: Although CoCr particles affect the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome-associated genes, a single stimulus was not sufficient to prime and activate the inflammasome. TNF was able to prime the NLRP3 inflammasome of human osteoblasts.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; human osteoblasts; joint replacement; metallic particles; osteolysis.
Copyright © 2024 Sellin, Hansmann, Bader and Jonitz-Heincke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

