New insights into mechanisms and interventions of locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38751435
- PMCID: PMC11090796
- DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2024.02.06
New insights into mechanisms and interventions of locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
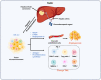
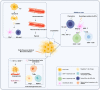
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is responsible for a significant number of cancer-related deaths worldwide and its incidence is increasing. Locoregional treatments, which are precision procedures guided by imaging to specifically target liver tumors, play a critical role in the management of a substantial portion of HCC cases. These therapies have become an essential element of the HCC treatment landscape, with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) being the treatment of choice for patients with intermediate to advanced stages of the disease. Other locoregional therapies, like radiofrequency ablation, are highly effective for small, early-stage HCC. Nevertheless, the advent of targeted immunotherapy has challenged these established treatments. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have shown remarkable efficacy in clinical settings. However, their specific uses and the development of resistance in subsequent treatments have led clinicians to reevaluate the future direction of HCC therapy. This review concentrates on the distinct features of both systemic and novel locoregional therapies. We investigate their effects on the tumor microenvironment at the molecular level and discuss how targeted immunotherapy can be effectively integrated with locoregional therapies. We also examine research findings from retrospective studies and randomized controlled trials on various combined treatment regimens, assessing their validity to determine the future evolution of locoregional therapies within the framework of personalized, comprehensive treatment.
Keywords: Locoregional therapies; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy; transarterial chemoembolization; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright ©2024 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strategies to Improve the Antitumor Effect of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 26;12:783236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.783236. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locoregional therapies in the era of molecular and immune treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May;18(5):293-313. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00395-0. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33510460 Review.
-
Locoregional Combined With Systemic Therapies for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Inevitable Trend of Rapid Development.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 13;8:635243. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.635243. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33928118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination therapies plus transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: a snapshot of clinical trial progress.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022 Apr;31(4):379-391. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2022.2008355. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34788184 Review.
-
A Recent Advance in Image-Guided Locoregional Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Gastrointest Tumors. 2016 Oct;3(2):90-102. doi: 10.1159/000445888. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Gastrointest Tumors. 2016. PMID: 27904861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of regorafenib combined with immunotherapy and arterial chemoembolization on the survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Mar 15;17(3):1962-1973. doi: 10.62347/BXYO6569. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40226031 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis identifies PLAG1 as a key regulator of tumor immune microenvironment and prognostic biomarker.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 10;16:1572108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1572108. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40276502 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation of C6orf120 as a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target for liver hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomol Biomed. 2025 Mar 7;25(4):925-939. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.11246. Biomol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 39388711 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of the Multi-Level Comprehensive Collateral Artery Embolism Sequential Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy, Combined with TKI and ICI, for Unresectable Huge Hepatocellular Carcinoma (>10cm): A Propensity Score Matching Cohort Study.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025 Aug 19;12:1821-1834. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S546588. eCollection 2025. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025. PMID: 40861310 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted activation of junctional adhesion molecule-like protein+ CD8+ T cells enhances immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma.Chin J Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 30;37(2):212-226. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2025.02.08. Chin J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40353078 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
