Postoperative radiotherapy versus surgery alone in pN1 oral cavity cancer patients: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 38751691
- PMCID: PMC11094775
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.1260
Postoperative radiotherapy versus surgery alone in pN1 oral cavity cancer patients: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this meta-analysis is to evaluate the potential benefits of postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) in patients with pN1 oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma.
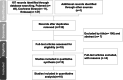
Methods: A literature search through major databases was conducted until January 2023. The adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) or risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of different survival outcomes were extracted and pooled.
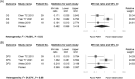
Results: Ten studies published between 2005 and 2022, with a pooled patient population of 2888, were included in this meta-analysis. Due to differences in study design and reported outcomes, the studies were categorized into distinct groups. In pN1 patients without extranodal extension (ENE), PORT was associated with a significant improvement in overall survival (OS) (aHR 0.76, 95% CI: 0.61-0.94). In pN1 patients without ENE and positive margins, PORT improved OS (aHR 0.71, 95% CI: 0.56-0.89) and was associated with a lower regional recurrence rate (RR 0.35, 95% CI: 0.15-0.83). However, in pN1 patients without ENE, positive margins, perineural invasion, and lymphovascular invasion, there were no significant differences observed between the PORT and observation groups in either 5-year OS (RR 0.48, 95% CI: 0.07-3.41) or 5-year disease-free survival (RR 0.37, 95% CI: 0.07-2.06).
Conclusions: The current study demonstrated that PORT has the potential to improve OS in pN1 disease. However, the decision of whether to administer PORT still hinges on diverse clinical scenarios, and additional research is necessary to furnish a more conclusive resolution.
Level of evidence: 2.
Keywords: OSCC; PORT; adjuvant therapy; oral cancer; postoperative radiotherapy; squamous cell carcinoma.
© 2024 The Authors. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Triological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Funk GF, Karnell LH, Robinson RA, Zhen WK, Trask DK, Hoffman HT. Presentation, treatment, and outcome of oral cavity cancer: a National Cancer Data Base report. Head Neck. 2002;24:165‐180. - PubMed
-
- Shield KD, Ferlay J, Jemal A, et al. The global incidence of lip, oral cavity, and pharyngeal cancers by subsite in 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:51‐64. - PubMed
-
- Massano J, Regateiro FS, Januário G, Ferreira A. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: review of prognostic and predictive factors. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102:67‐76. - PubMed
-
- Amit M, Yen TC, Liao CT, et al. Clinical nodal stage is a significant predictor of outcome in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma and pathologically negative neck metastases: results of the international consortium for outcome research. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:3575‐3581. - PubMed
-
- Liao CT, Hsueh C, Lee LY, et al. Neck dissection field and lymph node density predict prognosis in patients with oral cavity cancer and pathological node metastases treated with adjuvant therapy. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:329‐336. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
