Investigating the L-Glu-NMDA receptor-H2S-NMDA receptor pathway that regulates gastric function in rats' nucleus ambiguus
- PMID: 38751777
- PMCID: PMC11094298
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1389873
Investigating the L-Glu-NMDA receptor-H2S-NMDA receptor pathway that regulates gastric function in rats' nucleus ambiguus
Abstract
Background: In previous investigations, we explored the regulation of gastric function by hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and L-glutamate (L-Glu) injections in the nucleus ambiguus (NA). We also determined that both H2S and L-Glu have roles to play in the physiological activities of the body, and that NA is an important nucleus for receiving visceral sensations. The purpose of this study was to explore the potential pathway link between L-Glu and H2S, resulting in the regulation of gastric function.
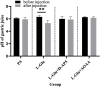
Methods: Physiological saline (PS), L-glutamate (L-Glu, 2 nmol), NaHS (2 nmol), D-2-amino-5-phopho-novalerate (D-AP5, 2 nmol) + L-Glu (2 nmol), aminooxyacetic acid (AOAA, 2 nmol) + L-Glu (2 nmol), D-AP5 (2 nmol) + NaHS (2 nmol) were injected into the NA. A balloon was inserted into the stomach to observe gastric pressure and for recording the changes of gastric smooth muscle contraction curve. The gastric fluid was collected by esophageal perfusion and for recording the change of gastric pH value.
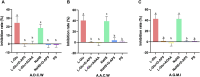
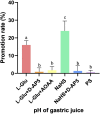
Results: Injecting L-Glu in NA was found to significantly inhibit gastric motility and promote gastric acid secretion in rats (p < 0.01). On the other hand, injecting the PS, pre-injection N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor blocker D-AP5, cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) inhibitor AOAA and re-injection L-Glu did not result in significant changes (p > 0.05). The same injection NaHS significantly inhibit gastric motility and promote gastric acid secretion in rats (p < 0.01), but is eliminated by injection D-AP5 (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: The results indicate that both exogenous L-Glu and H2S injected in NA regulate gastric motility and gastric acid secretion through NMDA receptors. This suggests that NA has an L-Glu-NMDA receptor-CBS-H2S pathway that regulates gastric function.
Keywords: L-glutamate; gastric acid secretion; gastric motility; hydrogen sulfide; nucleus ambiguus.
Copyright © 2024 Sun, Li, Shi, Wang, Li, Fan, Yu, Ji, Gao, Hou and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects and mechanisms of L-glutamate microinjected into nucleus ambiguus on gastric motility in rats.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010 Apr 20;123(8):1052-7. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010. PMID: 20497713
-
Effects of Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus on Gastric Function in Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 13;12:806012. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.806012. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35095514 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Within the Nucleus Ambiguus Inhibits Gastrointestinal Motility in Rats.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 11;11:545184. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.545184. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33013478 Free PMC article.
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24239876 Review.
-
Biological and Analytical Perspectives on D-Amino Acids in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 9;18(5):705. doi: 10.3390/ph18050705. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S- or H2Sn-Polysulfides) in Synaptic Plasticity: Modulation of NMDA Receptors and Neurotransmitter Release in Learning and Memory.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 28;26(7):3131. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073131. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

