Characterization of Ocular Sonography Findings and their Relationship to Clinical Features from a South Indian Cohort of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
- PMID: 38751906
- PMCID: PMC11093174
- DOI: 10.4103/aian.aian_1057_23
Characterization of Ocular Sonography Findings and their Relationship to Clinical Features from a South Indian Cohort of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) typically manifests with headache, accompanied by papilledema and visual loss, and has a higher prevalence in females. In recent years, ocular sonography, particularly, measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD), is being investigated for diagnosis of IIH.
Methods: A total of 35 patients over the age of 18 years, fulfilling the modified Dandy's criteria for diagnosis of IIH were included. Patients underwent assessment with magnetic resonance imaging, lumbar puncture, and ocular sonography to measure ONSD and ocular arterial indices.
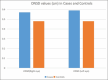
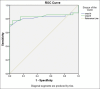
Results: The mean ONSD values (in centimeters) in the right eye of patients with IIH was 0.57 ± 0.13, while it was 0.48 ± 0.03 in controls. In the left eye, the mean ONSD value (cm) was 0.59 ± 0.13 in patients with IIH and 0.48 ± 0.03 in controls. ONSD was significantly higher in cases compared to controls (P < 0.001, Welch test). Pulsatility index of the central retinal artery was significantly higher in cases compared to controls (P < 0.001, Welch test). Resistance index of the ophthalmic artery was statistically significant (P < 0.005, Welch test). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis revealed a cutoff value of 5.1 mm on the right side and 5 mm on the left side had a sensitivity and specificity of more than 80% for IIH diagnosis.
Conclusion: Our study provides insights into the utility of optic nerve sheath measurements and arterial indices in the diagnosis of IIH in a South Indian cohort. Further research is needed to fully understand the longitudinal relationship of these parameters and treatment outcomes in IIH.
Keywords: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension; ONSD; ocular ultrasound.
Copyright: © 2024 Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sonographic assessment of optic nerve and ophthalmic vessels in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension.Neurol Res. 2018 Sep;40(9):728-735. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2018.1473097. Epub 2018 May 25. Neurol Res. 2018. PMID: 29799769
-
Comparison of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameters Measured by Optic Ultrasonography Before and After Lumbar Puncture in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Patients.Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2023 May 5;60(2):117-123. doi: 10.29399/npa.28074. eCollection 2023. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2023. PMID: 37287564 Free PMC article.
-
Sonographic assessment of the optic nerve and the central retinal artery in idiopathic intracranial hypertension.J Clin Neurosci. 2020 Feb;72:292-297. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2019.09.003. Epub 2019 Sep 17. J Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31540860
-
Transorbital sonography in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Single-center study, systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neuroimaging. 2024 Jan-Feb;34(1):108-119. doi: 10.1111/jon.13160. Epub 2023 Oct 11. J Neuroimaging. 2024. PMID: 37822030
-
B-Mode Transorbital Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ultraschall Med. 2019 Apr;40(2):247-252. doi: 10.1055/a-0719-4903. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Ultraschall Med. 2019. PMID: 30347420 English.
References
-
- Hoffmann J, Goadsby PJ. Update on intracranial hypertension and hypotension. Curr Opin Neurol. 2013;26:240–7. - PubMed
-
- Janitschke D, Stögbauer J, Lattanzi S, Brigo F, Lochner P. B-mode transorbital ultrasonography for the diagnosis of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci. 2023;44:4313–22. - PubMed