Pontine Tegmental Cap Dysplasia: A Rare Brainstem Malformation Mimicking Hereditary Sensory Autonomic Neuropathy
- PMID: 38751914
- PMCID: PMC11093181
- DOI: 10.4103/aian.aian_781_23
Pontine Tegmental Cap Dysplasia: A Rare Brainstem Malformation Mimicking Hereditary Sensory Autonomic Neuropathy
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
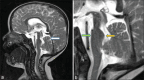
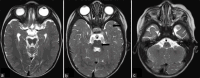
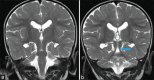
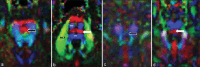
Figures

References
-
- Barth PG, Majoie CB, Caan MW, Weterman MA, Kyllerman M, Smit LM, et al. Pontine tegmental cap dysplasia: A novel brain malformation with a defect in axonal guidance. Brain. 2007;130:2258–66. - PubMed
-
- Picker-Minh S, Hartenstein S, Proquitté H, Fröhler S, Raile V, Kraemer N, et al. Pontine tegmental cap dysplasia in an extremely preterm infant and review of the literature. J Child Neurol. 2017;32:334–40. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi JM, Sankhe S, Udmale P. Pontine tegmental cap dysplasia- the role of MRI and DTI in diagnosis. Neurol India. 2020;68:691–3. - PubMed
-
- Macferran KM, Buchmann RF, Ramakrishnaiah R, Griebel ML, Sanger WG, Saronwala A, et al. Pontine tegmental cap dysplasia with a 2q13 microdeletion involving the NPHP1 gene: Insights into malformations of the mid-hindbrain. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2010;17:69–74. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

