A preclinical animal study to evaluate the operability and safety of domestic one-way endobronchial valves
- PMID: 38751979
- PMCID: PMC11094200
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1293940
A preclinical animal study to evaluate the operability and safety of domestic one-way endobronchial valves
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the operability and safety of bronchoscopic domestic one-way endobronchial valves (EBV) on animals.
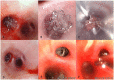
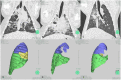
Methods: Nine pigs were randomly assigned (2:1) to receive domestic one-way EBV (the experimental group, n = 6) and Zephyr® EBV (the control group, n = 3). Routine blood tests, arterial blood gases, and CT scans of the lungs were performed 1 day pre-procedure in addition to 1 week and 1 month post-procedure to assess changes in blood markers and lung volumes. At 1 month post-procedure, the animals were sacrificed, followed by removal of all valves via bronchoscopy. Pathological examinations of critical organs were subsequently performed.
Results: A total of 15 valves were placed in the experimental group and 6 valves were placed in the control group, without serious complications. Routine blood tests and arterial blood gas examinations at 1 day pre-procedure, 1 week post-procedure, and 1 month post-procedure did not differ significantly in both groups. No EBV displacement was noted under bronchoscopy, and the valve was smoothly removable by bronchoscope at 1 month post-procedure. At 1 week post-procedure, varying degrees of target lung lobe volume reduction were observed on lung CT in both groups. Lung volume reduction was achieved at 1 month post-procedure in both groups, without significant statistical difference. Although 3 cases in the experimental group and 1 case in the control group developed varying degrees of pneumonia, the inflammatory response did not increase over time during the experimental period. Pathological examination revealed no significant abnormal changes in the critical organs for both groups.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that domestic EBV is safe and reliable for endobronchial application in general-grade laboratory white pigs. The safety of domestic EBV is similar to that of Zephyr® EBV, with good ease of use and operability. This kind of domestic EBV can meet the safety evaluation requirements for animal testing.
Keywords: animal; bronchoscopy; emphysema; lung volume reduction; one-way endobronchial valve; operability; safety.
Copyright © 2024 Jiao, Tian, Liu, Shen, Wang, Li, Zhang, Dong, Li, Bai and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Endobronchial Valve (Zephyr) Treatment in Homogeneous Emphysema: One-Year Results from the IMPACT Randomized Clinical Trial.Respiration. 2021;100(12):1174-1185. doi: 10.1159/000517034. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Respiration. 2021. PMID: 34350884 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Endobronchial valves: 1st Multicenter retrospective study on the 2-step approach.Respir Med Res. 2023 Jun;83:100957. doi: 10.1016/j.resmer.2022.100957. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Respir Med Res. 2023. PMID: 36630778
-
When Treatment of Pulmonary Emphysema with Endobronchial Valves Did Not Work: Evaluation of Quantitative CT Analysis and Pulmonary Function Tests Before and After Valve Explantation.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022 Oct 11;17:2553-2566. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S367667. eCollection 2022. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022. PMID: 36304970 Free PMC article.
-
From plugging air leaks to reducing lung volume: a review of the many uses of endobronchial valves.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2023 Jul-Dec;20(9):721-727. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2023.2233435. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2023. PMID: 37409351 Review.
-
Device profile of the Zephyr endobronchial valve in heterogenous emphysema: overview of its safety and efficacy.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2021 Sep;18(9):823-832. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2021.1957831. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2021. PMID: 34314290 Review.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease . (2023), Global strategy for prevention, diagnosis and management of COPD: 2023 report. Available at: https://goldcopd.org/2023-gold-report-2/
-
- Adeloye D, Song P, Zhu Y, Campbell H, Sheikh A, Rudan I. Global, regional, and national prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in 2019: a systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Respir Med. (2022) 10:447–58. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00511-7, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

