Effects of Cranberry Extract (Vaccinium macrocarpon) Supplementation on Lipid Peroxidation and Inflammation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (Stages 3-4): A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 38752013
- PMCID: PMC11095989
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/9590066
Effects of Cranberry Extract (Vaccinium macrocarpon) Supplementation on Lipid Peroxidation and Inflammation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (Stages 3-4): A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Growing evidence suggests that bioactive compounds in berry fruits may mitigate inflammation in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Objectives: To evaluate cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) supplementation effects on modulation of transcription factors involved in inflammation and oxidative stress in nondialysis (stages 3 and 4) patients with CKD. Design/Participants. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was performed with 30 patients to receive capsules containing cranberry extract (1000 mg/day) or placebo (1000 mg/day of corn starch) for two months. Measurements. The mRNA expression of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) and nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB) was evaluated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) were measured in the plasma to assess oxidative stress. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) plasma levels were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and C-reactive protein (CRP) by immunoturbidimetric method.
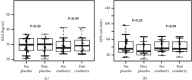
Results: Twenty-five patients completed the study: 12 in the cranberry group (56.7 ± 7.5 years and body mass index (BMI) of 29.6 ± 5.5 kg/m2) and 13 in the placebo group (58.8 ± 5.1 years and BMI 29.8 ± 5.4 kg/m2). There were no differences in NF-kB or Nrf2 mRNA expressions (p = 0.99 and p = 0.89) or TBARS, CRP, and IL-6 plasma levels after cranberry supplementation.
Conclusions: The cranberry extract administration (1000 mg/day) did not affect Nrf2 and NF-kB mRNA expression, oxidative stress, or inflammatory markers levels in nondialysis CKD patients. This trial is registered with NCT04377919.
Copyright © 2024 Laís de Souza Gouveia Moreira et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest or personal relationships could interfere with the research.
Figures


References
-
- Ke C., Liang J., Liu M., Liu S., Wang C. Burden of chronic kidney disease and its risk-attributable burden in 137 low-and middle-income countries, 1990–2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMC Nephrology . 2022;23(1):17–12. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02597-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rapa S. F., Di Iorio B. R., Campiglia P., Heidland A., Marzocco S. Inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease-potential therapeutic role of minerals, vitamins and plant-derived metabolites. International Journal of Molecular Sciences . 2019;21(1):p. 263. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010263. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

