Distinct Patterns of Liver Chemistry Changes in Pediatric Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Origin and COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38752102
- PMCID: PMC11094484
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.58307
Distinct Patterns of Liver Chemistry Changes in Pediatric Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Origin and COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review
Abstract
In 2021 and 2022, there were noted to be clusters of pediatric acute hepatitis of unknown origin (AHUO) occurring across the globe. While there was not necessarily a global increase in cases, understanding the pattern of liver injury in AHUO is crucial to properly identify cases of this unexplained phenomenon, especially since it occurred simultaneously with a global resurgence of COVID-19. The objective of this study was to contrast the patterns in liver-relevant biochemical data from COVID-19 patients and AHUO. Studies reporting liver chemistries for cases of AHUO and COVID-19 were identified by a systematic review and search of the literature. For each case, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, and international normalized ratio (INR) levels were extracted as available. These were normalized to multiples of the upper limit of normal by patient age. There were statistically significant greater elevations of ALT and AST in patients with AHUO than in those with COVID-19. Only a subset of patients with COVID-19 had an AST or ALT greater than the normal range. INR elevation could be substantial for both conditions but was also statistically higher in the AHUO group. Liver chemistry changes were not statistically correlated with age. The pattern of liver chemistry changes between AHUO and COVID-19 have some distinctions, which suggests that AHUO is not a phenomenon driven primarily by SARS-CoV-2 infection alone. Differentiating AHUO and COVID-19 would be challenging based on patterns of liver chemistry changes alone.
Keywords: disease outbreak; emerging communicable diseases; liver disease etiology; liver failure; pediatric hepatology.
Copyright © 2024, Van Wylick et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
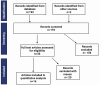
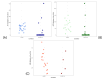
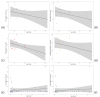
References
-
- Severe hepatitis outbreak in children linked to AAV2 virus. Tacke F. Nature. 2023;617:471–472. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
