Tryptophan in the mouse diet is essential for embryo implantation and decidualization
- PMID: 38752181
- PMCID: PMC11094255
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356914
Tryptophan in the mouse diet is essential for embryo implantation and decidualization
Abstract
Introduction: Nutritional deficiency occurs frequently during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Tryptophan (Trp), an essential amino acid which is critical for protein synthesis, serves as the precursor for serotonin, melatonin, and kynurenine (Kyn). The imbalance between serotonin and kynurenine pathways in Trp metabolism is closely related to inflammation and depression. This study assessed the effects of Trp deficiency on mouse early pregnancy.
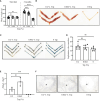
Methods: Embryo implantation and decidualization were analyzed after female mice had been fed diets containing 0.2% Trp (for the control group), 0.062% Trp (for the low Trp group) and 0% Trp (for the Trp-free group) for two months. The uteri of the mice were collected on days 4, 5, and 8 of pregnancy for further analysis.
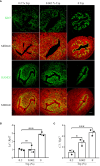
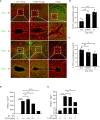
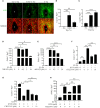
Results: On day 8 of pregnancy, the number of implantation sites were found to be similar between the control and the low Trp groups. However, no implantation sites were detected in the Trp-free group. On day 5 of pregnancy, plane polarity- and decidualization-related molecules showed abnormal expression pattern in the Trp-free group. On day 4 of pregnancy, there was no significant difference in uterine receptivity molecules between the low-Trp group and the control group, but uterine receptivity was abnormal in the Trp-free group. At implantation sites of the Trp-free group, IDO and AHR levels were markedly elevated. This potentially increased levels of Kyn, 2-hydroxy estradiol, and 4-hydroxy estradiol to affect decidualization.
Conclusions: Trp-free diet may impair decidualization via the IDO-KYN-AHR pathway.
Keywords: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; decidualization; tryptophan deficiency; uterine receptivity; uterus.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Ran, Shi, Liu, Wang, Luo and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Studies using the estrogen receptor alpha knockout uterus demonstrate that implantation but not decidualization-associated signaling is estrogen dependent.Biol Reprod. 2002 Oct;67(4):1268-77. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod67.4.1268. Biol Reprod. 2002. PMID: 12297545
-
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin-Stimulated Interleukin-4-Induced-1 (IL4I1) Promotes Human Decidualization via Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3163. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043163. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834576 Free PMC article.
-
Increased uterine androgen receptor protein abundance results in implantation and mitochondrial defects in pregnant rats with hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Oct;99(10):1427-1446. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02104-z. Epub 2021 Jun 28. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34180022 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on the Role of Estrogen and Progesterone Signaling in Mouse Embryo Implantation and Decidualization.Reprod Sci. 2023 Jun;30(6):1746-1757. doi: 10.1007/s43032-023-01169-0. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 36694081 Review.
-
The end of the road for the tryptophan depletion concept in pregnancy and infection.Clin Sci (Lond). 2016 Aug 1;130(15):1327-33. doi: 10.1042/CS20160153. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016. PMID: 27358028 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Diethylstilbestrol on Implantation and Decidualization in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 26;26(9):4122. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094122. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362361 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

