Eosinophilic esophagitis: Current concepts in diagnosis and management
- PMID: 38752302
- PMCID: PMC11379248
- DOI: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_50_24
Eosinophilic esophagitis: Current concepts in diagnosis and management
Abstract
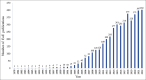
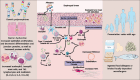
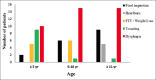
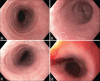
Eosinophilic esophagitis is an antigen-mediated chronic inflammatory disorder that has risen in incidence and prevalence over the past 2 decades. The clinical presentation is variable and consists of mainly esophageal symptoms such as dysphagia, heartburn, food impaction, and vomiting. Current management relies on dietary elimination, proton-pump inhibitors, and topical corticosteroids with different response rates and relapses after treatment discontinuation. With a better understanding of the underlying pathophysiology, many molecules emerged recently as targeted treatment including dupilumab (IL4/IL13 blocker), as the first FDA-approved biological treatment, which has changed the management paradigm.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Evan S. Dellon, MD MPH
Research funding: Adare/Ellodi, Allakos, Arena/Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Eupraxia, Ferring, GSK, Meritage, Miraca, Nutricia, Celgene/Receptos/BMS, Regeneron, Revolo, Shire/Takeda
Consultant: Abbott, Abbvie, Adare/Ellodi, Aimmune, Akesobio, Alfasigma, ALK, Allakos, Amgen, Aqilion, Arena/Pfizer, Aslan, AstraZeneca, Avir, Biorasi, Calypso, Celgene/Receptos/BMS, Celldex, Eli Lilly, EsoCap, Eupraxia, Dr. Falk Pharma, Ferring, GSK, Gossamer Bio, Holoclara, Invea, Knightpoint, Landos, LucidDx, Morphic, Nexstone Immunology/Uniquity, Nutricia, Parexel/Calyx, Phathom, Regeneron, Revolo, Robarts/Alimentiv, Salix, Sanofi, Shire/Takeda, Target RWE, Upstream Bio
Educational grant: Allakos, Aqilion, Holoclara, Invea.
The other authors reported no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis in children: new kids on the block.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2025 Jul;26(10):1117-1132. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2025.2517801. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40490426 Review.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Adults.Am J Med. 2016 Sep;129(9):924-34. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.04.024. Epub 2016 May 4. Am J Med. 2016. PMID: 27155108 Review.
-
Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Dietary and Nondietary Approaches.Nutr Clin Pract. 2020 Oct;35(5):835-847. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10571. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Nutr Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32822071 Review.
-
Patient-reported symptoms and burden of eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence from real-world clinical practice.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug 3;24(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03334-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39097693 Free PMC article.
-
[Dietary and pharmacological aspects of eosinophilic esophagitis].Orv Hetil. 2015 Jun 7;156(23):927-32. doi: 10.1556/650.2015.30164. Orv Hetil. 2015. PMID: 26027600 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Emerging Insights Into Diagnosis and Management.Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2025 Jun;25(2):117-125. doi: 10.7704/kjhugr.2025.0013. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2025. PMID: 40550543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adherence to clinical guidelines for the evaluation and management of eosinophilic esophagitis among gastroenterologists in the Arab countries.Front Pediatr. 2025 Apr 10;13:1521266. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1521266. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40276102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clayton F, Peterson K. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Pathophysiology and definition. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2018;28:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2017.07.011. - PubMed
-
- Straumann A, Spichtin HP, Bernoulli R, Loosli J, Vögtlin J. [Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis: A frequently overlooked disease with typical clinical aspects and discrete endoscopic findings. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1994;124:1419–29. - PubMed
-
- Landres RT, Kuster GG, Strum WB. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology. 1978;74:1298–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

