Machine learning framework to predict pharmacokinetic profile of small molecule drugs based on chemical structure
- PMID: 38752574
- PMCID: PMC11097621
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13824
Machine learning framework to predict pharmacokinetic profile of small molecule drugs based on chemical structure
Abstract
Accurate prediction of a new compound's pharmacokinetic (PK) profile is pivotal for the success of drug discovery programs. An initial assessment of PK in preclinical species and humans is typically performed through allometric scaling and mathematical modeling. These methods use parameters estimated from in vitro or in vivo experiments, which although helpful for an initial estimation, require extensive animal experiments. Furthermore, mathematical models are limited by the mechanistic underpinning of the drugs' absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) which are largely unknown in the early stages of drug discovery. In this work, we propose a novel methodology in which concentration versus time profile of small molecules in rats is directly predicted by machine learning (ML) using structure-driven molecular properties as input and thus mitigating the need for animal experimentation. The proposed framework initially predicts ADME properties based on molecular structure and then uses them as input to a ML model to predict the PK profile. For the compounds tested, our results demonstrate that PK profiles can be adequately predicted using the proposed algorithm, especially for compounds with Tanimoto score greater than 0.5, the average mean absolute percentage error between predicted PK profile and observed PK profile data was found to be less than 150%. The suggested framework aims to facilitate PK predictions and thus support molecular screening and design earlier in the drug discovery process.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were employed by Sanofi while the manuscript was written. The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures
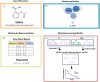

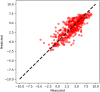


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Application of machine learning in combination with mechanistic modeling to predict plasma exposure of small molecules.Front Syst Biol. 2023 Jun 20;3:1180948. doi: 10.3389/fsysb.2023.1180948. eCollection 2023. Front Syst Biol. 2023. PMID: 40809487 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Approaches for predicting dairy cattle methane emissions: from traditional methods to machine learning.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae219. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae219. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39123286 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Refined ADME Profiles for ATC Drug Classes.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 28;17(3):308. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030308. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40142973 Free PMC article.
-
Computational approaches for toxicology and Pharmacokinetic properties prediction.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2025 Sep 4;52(5):51. doi: 10.1007/s10928-025-09999-y. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2025. PMID: 40908375 Review.
-
Predicting Pharmacokinetics in Rats Using Machine Learning: A Comparative Study Between Empirical, Compartmental, and PBPK-Based Approaches.Clin Transl Sci. 2025 Mar;18(3):e70150. doi: 10.1111/cts.70150. Clin Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40091606 Free PMC article.
-
The dawn of a new era: can machine learning and large language models reshape QSP modeling?J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2025 Jun 16;52(4):36. doi: 10.1007/s10928-025-09984-5. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2025. PMID: 40524056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of human pharmacokinetic parameters incorporating SMILES information.Arch Pharm Res. 2024 Dec;47(12):914-923. doi: 10.1007/s12272-024-01520-2. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Arch Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 39589671
References
-
- Cella M, Gorter de Vries F, Burger D, Danhof M, Della Pasqua O. A model‐based approach to dose selection in early pediatric development. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;87(3):294‐302. - PubMed
-
- Stewart A, Denoyer D, Gao X, Toh YC. The FDA modernisation act 2.0: bringing non‐animal technologies to the regulatory table. Drug Discov Today. 2023;28(4):103496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

