Antibody persistence to diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, Bordetella pertussis antigens, and Haemophilus influenzae type b following primary and first booster with pentavalent versus hexavalent vaccines
- PMID: 38752802
- PMCID: PMC11789732
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2352909
Antibody persistence to diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, Bordetella pertussis antigens, and Haemophilus influenzae type b following primary and first booster with pentavalent versus hexavalent vaccines
Abstract
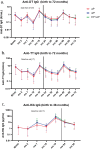
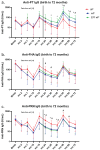
Thailand has incorporated the whole-cell (wP) pertussis vaccine into the expanded program on immunization since 1977 and has offered the acellular pertussis (aP) vaccine as an optional vaccine for infants since 2001. We followed healthy children from a clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02408926) in which children were randomly assigned to receive either pentavalent (DTwP-HB-Hib) or hexavalent (DTaP-IPV-HB-Hib) vaccines for their primary series (administered at 2, 4, and 6 months) and first booster vaccination (18 months). Both groups received Tdap-IPV as a second booster at the age of 4 y. Blood samples were collected for evaluation of antibody persistence to diphtheria toxoid (DT), tetanus toxoid (TT), and Bordetella pertussis (B. pertussis) between 2 and 6 y of age annually, and for the immunogenicity study of Tdap-IPV at 1 month after the second booster. Antibody persistence to Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) was followed until 3 y of age. A total of 105 hexavalent-vaccinated children and 91 pentavalent-vaccinated children completed this study. Both pentavalent and hexavalent groups demonstrated increased antibody levels against DT, TT, and B. pertussis antigens following the second booster with Tdap-IPV. All children achieved a seroprotective concentration for anti-DT and anti-TT IgG at 1 month post booster. The hexavalent group possessed significantly higher anti-pertactin IgG (adjusted p = .023), whereas the pentavalent group possessed significantly higher anti-pertussis toxin IgG (adjusted p < .001) after the second booster. Despite declining levels post-second booster, a greater number of children sustained protective levels of anti-DT and anti-TT IgG compared to those after the first booster.
Keywords: Diphtheria; Haemophilus influenzae type b; acellular; childhood; pertussis; tetanus; vaccine antibody; whole cell.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- WHO . SAGE pertussis working group: background paper. SAGE; 2014. Apr [accessed 2023 Nov 27]. https://terrance.who.int/mediacentre/data/sage/SAGE_Docs_Ppt_Apr2014/8_s....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
