[Interoperability Working Group: core dataset and information systems for data integration and data exchange in the Medical Informatics Initiative]
- PMID: 38753022
- PMCID: PMC11166738
- DOI: 10.1007/s00103-024-03888-4
[Interoperability Working Group: core dataset and information systems for data integration and data exchange in the Medical Informatics Initiative]
Abstract
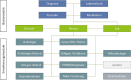
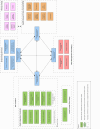
The interoperability Working Group of the Medical Informatics Initiative (MII) is the platform for the coordination of overarching procedures, data structures, and interfaces between the data integration centers (DIC) of the university hospitals and national and international interoperability committees. The goal is the joint content-related and technical design of a distributed infrastructure for the secondary use of healthcare data that can be used via the Research Data Portal for Health. Important general conditions are data privacy and IT security for the use of health data in biomedical research. To this end, suitable methods are used in dedicated task forces to enable procedural, syntactic, and semantic interoperability for data use projects. The MII core dataset was developed as several modules with corresponding information models and implemented using the HL7® FHIR® standard to enable content-related and technical specifications for the interoperable provision of healthcare data through the DIC. International terminologies and consented metadata are used to describe these data in more detail. The overall architecture, including overarching interfaces, implements the methodological and legal requirements for a distributed data use infrastructure, for example, by providing pseudonymized data or by federated analyses. With these results of the Interoperability Working Group, the MII is presenting a future-oriented solution for the exchange and use of healthcare data, the applicability of which goes beyond the purpose of research and can play an essential role in the digital transformation of the healthcare system.
Die Arbeitsgruppe Interoperabilität der Medizininformatik-Initiative (MII) ist die Plattform für die Abstimmung übergreifender Vorgehensweisen, Datenstrukturen und Schnittstellen zwischen den Datenintegrationszentren (DIZ) der Universitätskliniken und nationalen bzw. internationalen Interoperabilitätsgremien. Ziel ist die gemeinsame inhaltliche und technische Ausgestaltung einer über das Forschungsdatenportal für Gesundheit nutzbaren verteilten Infrastruktur zur Sekundärnutzung klinischer Versorgungsdaten. Wichtige Rahmenbedingungen sind dabei Datenschutz und IT-Sicherheit für die Nutzung von Gesundheitsdaten in der biomedizinischen Forschung. Hierfür werden in dezidierten Taskforces geeignete Methoden eingesetzt, um prozessuale, syntaktische und semantische Interoperabilität für Datennutzungsprojekte zu ermöglichen. So wurde der MII-Kerndatensatz, bestehend aus mehreren Modulen mit zugehörigen Informationsmodellen, entwickelt und mittels des Standards HL7® FHIR® implementiert, um fachliche und technische Vorgaben für die interoperable Datenbereitstellung von Versorgungsdaten durch die DIZ zu ermöglichen. Zur näheren Beschreibung dieser Datensätze dienen internationale Terminologien und konsentierte Metadaten. Die Gesamtarchitektur, einschließlich übergreifender Schnittstellen, setzt die methodischen und rechtlichen Anforderungen an eine verteilte Datennutzungsinfrastruktur z. B. durch Bereitstellung pseudonymisierter Daten oder föderierte Analysen um. Mit diesen Ergebnissen der Arbeitsgruppe Interoperabilität stellt die MII eine zukunftsweisende Lösung für den Austausch und die Nutzung von Routinedaten vor, deren Anwendbarkeit über den Zweck der Forschung hinausgeht und eine wesentliche Rolle in der digitalen Transformation des Gesundheitswesens spielen kann.
Keywords: Data integration center; FHIR; Research data infrastructure; Secondary Use; Terminology services.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Geraci A, Katki F, McMonegal L, et al. IEEE standard computer dictionary: a compilation of IEEE standard computer glossaries, 610. New York: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers; 1991.
-
- Bruland P, Drepper J, Ganslandt T et al (2017) Gemeinsames Eckpunktepapier zur Interoperabilität. https://www.medizininformatik-initiative.de/sites/default/files/inline-f.... Zugegriffen: 10. Dez. 2023
-
- gematik (2023) Interop Council. https://www.ina.gematik.de/mitwirken/expertengremium. Zugegriffen: 11. Dez. 2023
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

