Accuracy of brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide for detecting paediatric pulmonary hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38753384
- PMCID: PMC11100439
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2352603
Accuracy of brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide for detecting paediatric pulmonary hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a life-threatening disease, especially in paediatric population. Symptoms of paediatric PH are non-specific. Accurate detection of paediatric PH is helpful for early treatment and mortality reduction. Therefore, we assessed the overall performance of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) for diagnosing PH in paediatric population.
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library and Embase databases were screened since their respective inceptions until August 2023. A bivariate random model and a hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic model were used together to evaluate and summarize the overall performance of BNP and NT-proBNP for diagnosing paediatric PH.
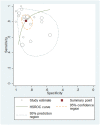
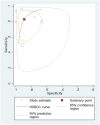
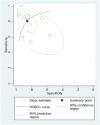
Results: Eighteen studies using BNP/NT-proBNP were assessed, comprising 1127 samples. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and area under the curve (AUROC) of BNP/NT-proBNP were separately as 0.81, 0.87, 6.33, 0.21, 29.50 and 0.91, suggesting a good diagnostic performance of BNP/NT-proBNP for detecting PH in paediatric population. For BNP, the pooled sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR, DOR and AUROC were 0.83, 0.89, 7.76, 0.19, 40.90 and 0.93, indicating the diagnostic accuracy of BNP for paediatric PH patients was good. For NT-proBNP, the pooled sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR, DOR and AUROC were 0.81, 0.86, 5.59, 0.22, 24.96 and 0.90, showing that NT-proBNP could provide a good value for detecting paediatric PH.
Conclusions: Both BNP and NT-proBNP are good markers for differentiating paediatric PH patients from non-PH individuals.
Keywords: N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide; Pulmonary hypertension; brain natriuretic peptide; paediatric; sensitivity; specificity.
Plain language summary
Accurate detection of paediatric PH is helpful for early treatment and mortality reduction. This study shows that both BNP and NT-proBNP are good markers for detecting paediatric PH. In clinical practice, we recommend that BNP and NT-proBNP are auxiliary biomarkers in diagnosing paediatric PH.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Natriuretic peptides in bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a systematic review.J Perinatol. 2020 Apr;40(4):607-615. doi: 10.1038/s41372-019-0588-2. Epub 2020 Jan 10. J Perinatol. 2020. PMID: 31925319
-
Brain natriuretic peptide as a predictive marker of mortality in sepsis: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Aug 7;24(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02661-z. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39112946 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic value of the currently used criteria and brain natriuretic peptide for diagnosing congestive heart failure in children with congenital heart disease].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Oct;44(10):728-32. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17229370 Chinese.
-
Prognostic value of plasma brain natriuretic peptide value for patientswith sepsis: A meta-analysis.J Crit Care. 2018 Dec;48:145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2018.08.040. Epub 2018 Aug 30. J Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30195194
-
Utility of B-type natriuretic peptides in the assessment of patients with systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary hypertension in the PHAROS registry.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017 Sep-Oct;35 Suppl 106(4):106-113. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27908301
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
