Oral glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and combinations of entero-pancreatic hormones as treatments for adults with type 2 diabetes: where are we now?
- PMID: 38753454
- PMCID: PMC11195668
- DOI: 10.1080/14656566.2024.2356254
Oral glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and combinations of entero-pancreatic hormones as treatments for adults with type 2 diabetes: where are we now?
Abstract
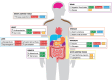
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (RAs) have changed the landscape of type 2 diabetes (T2D) management due to their cardio-renal benefits, their glucose-lowering efficacy and weight loss (WL) maintenance. However, the response to GLP-1 RA monotherapy is heterogeneous. Additionally, the majority of GLP-1 RAs are injectable treatments. Oral GLP-1 RAs and injectable combinations of GLP-1 with other entero-pancreatic hormones (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), glucagon and amylin) are under development for T2D and obesity management.
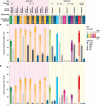
Areas covered: Herein, we review the data on (i) oral GLP-1 RAs (oral semaglutide 25/50 mg and orforglipron) and (ii) dual/triple agonists (tirzepatide, cagrilintide 2.4 mg/semaglutide 2.4 mg, survodutide, mazdutide, retatrutide) that have recently completed phase 3 trials for T2D or are currently in phase 3 clinical trials. Tirzepatide is the first approved dual agonist (GLP-1/GIP) for T2D and obesity management.
Expert opinion: We are in a new era in T2D management where entero-pancreatic hormone-based treatments can result in ≥15% WL and euglycemia for many people with T2D. Multiple molecules with different mechanisms of action are under development for T2D, obesity and other metabolic complications. Data on their cardio-renal benefits, long-term efficacy and safety as well as their cost-effectiveness will better inform their position in treatment algorithms.
Keywords: Cagrisema; obesity; orforglipron; retatrutide; semaglutide; survodutide; tirzepatide; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
D Papamargaritis has acted as a speaker for Novo Nordisk and has received grants from Novo Nordisk, Novo Nordisk UK Research Foundation, Academy of Medical Sciences/Diabetes UK, Health Education East Midlands and the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). M J Davies has acted as consultant, advisory board member and speaker for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi, an advisory board member Lexicon, Pfizer, ShouTi Pharma Inc, AstraZeneca, Zealand Pharma and Medtronic and as a speaker for AstraZeneca, Napp Pharmaceuticals, Novartis and Amgen. M J Davies has received grants from AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Sanofi-Aventis and Eli Lilly.
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet Lond Engl. 2023;402(10397):203–234. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
