The lethal K18-hACE2 knock-in mouse model mimicking the severe pneumonia of COVID-19 is practicable for antiviral development
- PMID: 38753462
- PMCID: PMC11132709
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2353302
The lethal K18-hACE2 knock-in mouse model mimicking the severe pneumonia of COVID-19 is practicable for antiviral development
Abstract
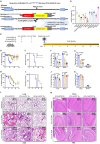
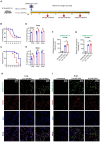
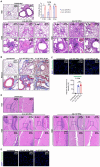
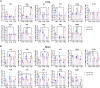
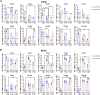
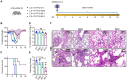
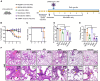
Animal models of COVID-19 facilitate the development of vaccines and antivirals against SARS-CoV-2. The efficacy of antivirals or vaccines may differ in different animal models with varied degrees of disease. Here, we introduce a mouse model expressing human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). In this model, ACE2 with the human cytokeratin 18 promoter was knocked into the Hipp11 locus of C57BL/6J mouse by CRISPR - Cas9 (K18-hACE2 KI). Upon intranasal inoculation with high (3 × 105 PFU) or low (2.5 × 102 PFU) dose of SARS-CoV-2 wildtype (WT), Delta, Omicron BA.1, or Omicron BA.2 variants, all mice showed obvious infection symptoms, including weight loss, high viral loads in the lung, and interstitial pneumonia. 100% lethality was observed in K18-hACE2 KI mice infected by variants with a delay of endpoint for Delta and BA.1, and a significantly attenuated pathogenicity was observed for BA.2. The pneumonia of infected mice was accompanied by the infiltration of neutrophils and pulmonary fibrosis in the lung. Compared with K18-hACE2 Tg mice and HFH4-hACE2 Tg mice, K18-hACE2 KI mice are more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2. In the antivirals test, REGN10933 and Remdesivir had limited antiviral efficacies in K18-hACE2 KI mice upon the challenge of SARS-CoV-2 infections, while Nirmatrelvir, monoclonal antibody 4G4, and mRNA vaccines potently protected the mice from death. Our results suggest that the K18-hACE2 KI mouse model is lethal and stable for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and is practicable and stringent to antiviral development.
Keywords: K18-hACE2 knock-in mouse; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; antivirals; mouse model; severe pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 Causes Lung Infection without Severe Disease in Human ACE2 Knock-In Mice.J Virol. 2022 Jan 12;96(1):e0151121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01511-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34668780 Free PMC article.
-
A human-ACE2 knock-in mouse model for SARS-CoV-2 infection recapitulates respiratory disorders but avoids neurological disease associated with the transgenic K18-hACE2 model.mBio. 2025 May 14;16(5):e0072025. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00720-25. Epub 2025 Apr 24. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40272151 Free PMC article.
-
The K18-Human ACE2 Transgenic Mouse Model Recapitulates Non-severe and Severe COVID-19 in Response to an Infectious Dose of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus.J Virol. 2022 Jan 12;96(1):e0096421. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00964-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34668775 Free PMC article.
-
K18- and CAG-hACE2 Transgenic Mouse Models and SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Neurodegeneration Research.Molecules. 2022 Jun 28;27(13):4142. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134142. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of S-protein RBD and hACE2 Interaction for Control of SARSCoV- 2 Infection (COVID-19).Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(6):689-703. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201117111259. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33208074 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 S protein disrupts the formation of ISGF3 complex through conserved S2 subunit to antagonize type I interferon response.J Virol. 2025 Jan 31;99(1):e0151624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01516-24. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 39699185 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing human ACE2 expression in mouse models to improve COVID-19 research.FEBS Open Bio. 2025 Feb;15(2):324-334. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13934. Epub 2024 Dec 29. FEBS Open Bio. 2025. PMID: 39737574 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 specific adaptations in N protein inhibit NF-κB activation and alter pathogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2025 Jan 6;224(1):e202404131. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202404131. Epub 2024 Dec 16. J Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39680116 Free PMC article.
-
A broad neutralizing nanobody against SARS-CoV-2 engineered from an approved drug.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jun 28;15(6):458. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06802-7. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38937437 Free PMC article.
-
SREBP1c-Mediated Transcriptional Repression of YME1L1 Contributes to Acute Kidney Injury by Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Tubular Epithelial Cells.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Feb;12(6):e2412233. doi: 10.1002/advs.202412233. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39680752 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
