Assessment of Gene Set Enrichment Analysis using curated RNA-seq-based benchmarks
- PMID: 38753612
- PMCID: PMC11098418
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302696
Assessment of Gene Set Enrichment Analysis using curated RNA-seq-based benchmarks
Abstract
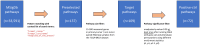
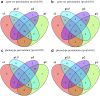
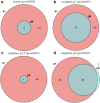
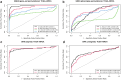
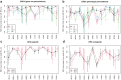
Pathway enrichment analysis is a ubiquitous computational biology method to interpret a list of genes (typically derived from the association of large-scale omics data with phenotypes of interest) in terms of higher-level, predefined gene sets that share biological function, chromosomal location, or other common features. Among many tools developed so far, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) stands out as one of the pioneering and most widely used methods. Although originally developed for microarray data, GSEA is nowadays extensively utilized for RNA-seq data analysis. Here, we quantitatively assessed the performance of a variety of GSEA modalities and provide guidance in the practical use of GSEA in RNA-seq experiments. We leveraged harmonized RNA-seq datasets available from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) in combination with large, curated pathway collections from the Molecular Signatures Database to obtain cancer-type-specific target pathway lists across multiple cancer types. We carried out a detailed analysis of GSEA performance using both gene-set and phenotype permutations combined with four different choices for the Kolmogorov-Smirnov enrichment statistic. Based on our benchmarks, we conclude that the classic/unweighted gene-set permutation approach offered comparable or better sensitivity-vs-specificity tradeoffs across cancer types compared with other, more complex and computationally intensive permutation methods. Finally, we analyzed other large cohorts for thyroid cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. We utilized a new consensus metric, the Enrichment Evidence Score (EES), which showed a remarkable agreement between pathways identified in TCGA and those from other sources, despite differences in cancer etiology. This finding suggests an EES-based strategy to identify a core set of pathways that may be complemented by an expanded set of pathways for downstream exploratory analysis. This work fills the existing gap in current guidelines and benchmarks for the use of GSEA with RNA-seq data and provides a framework to enable detailed benchmarking of other RNA-seq-based pathway analysis tools.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA-Seq and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs).Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2880:179-192. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4276-4_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39900759
-
Toward a gold standard for benchmarking gene set enrichment analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jan 18;22(1):545-556. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz158. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 32026945 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression analysis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using gene set enrichment analysis for biostatistical management.BJU Int. 2011 Jul;108(2 Pt 2):E29-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09794.x. Epub 2011 Mar 16. BJU Int. 2011. PMID: 21435154
-
Computational solutions for spatial transcriptomics.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Sep 1;20:4870-4884. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.043. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36147664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond standard pipeline and p < 0.05 in pathway enrichment analyses.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Jun;92:107455. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2021.107455. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33774420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of prognostic models based on cell cycle-related signatures for predicting the prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):2900-2915. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1479. Epub 2025 May 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40530147 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis in Zebrafish Embryos Is Susceptible to False-Positive Results in the Absence of Differentially Expressed Genes.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2025 Mar 4;19:11779322251321071. doi: 10.1177/11779322251321071. eCollection 2025. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2025. PMID: 40040651 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of DNAJC7 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by influencing the cell cycle and immune microenvironment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 May 2;151(5):154. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06202-0. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40312488 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression signatures of response to fluoxetine treatment: systematic review and meta-analyses.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 17. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-03118-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40676137
-
SomaModules: a pathway enrichment approach tailored to SomaScan data.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 2:2025.07.30.667673. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.30.667673. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Proteome Res. 2025 Aug 11. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c01114. PMID: 40766421 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

