Real-World Impact of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling on Biomarker Detection, Receipt of Therapy, and Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 38754057
- PMCID: PMC11371096
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.24.00075
Real-World Impact of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling on Biomarker Detection, Receipt of Therapy, and Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Therapeutic decision making for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (aNSCLC) includes a growing number of options for genomic, biomarker-guided, targeted therapies. We compared actionable biomarker detection, targeted therapy receipt, and real-world overall survival (rwOS) in patients with aNSCLC tested with comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP) versus small panel testing (SP) in real-world community health systems.
Methods: Patients older than 18 years diagnosed with aNSCLC between January 1, 2015, and December 31, 2020, who received biomarker testing were followed until death or study end (September 30, 2021), and categorized by most comprehensive testing during follow-up: SP (≤52 genes) or CGP (>52 genes).
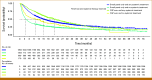
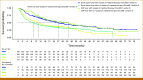
Results: Among 3,884 patients (median age, 68 years; 50% female; 73% non-Hispanic White), 20% received CGP and 80% SP. The proportion of patients with ≥one actionable biomarker (actionability) was significantly higher in CGP than in SP (32% v 14%; P < .001). Of patients with actionability, 43% (CGP) and 38% (SP) received matched therapies (P = .20). Among treated patients, CGP before first-line treatment was associated with higher likelihood of matched therapy in any line (odds ratio, 3.2 [95% CI, 1.84 to 5.53]). CGP testing (hazard ratio [HR], 0.80 [95% CI, 0.72 to 0.89]) and actionability (HR, 0.84 [95% CI, 0.77 to 0.91]) were associated with reduced risk of mortality. Among treated patients with actionability, matched therapy receipt showed improved median rwOS in months in CGP (34 [95% CI, 21 to 49] matched v 14 [95% CI, 10 to 18] unmatched) and SP (27 [95% CI, 21 to 43] matched v 10 [95% CI, 8 to 14] unmatched).
Conclusion: Patients who received CGP had improved detection of actionable biomarkers and greater use of matched therapies, both of which were associated with significant increases in survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Timely Comprehensive Genomic Profiling With Precision Oncology Treatment Use and Patient Outcomes in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2024 Mar;8:e2300292. doi: 10.1200/PO.23.00292. JCO Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38452312 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective analysis of real-world data to determine clinical outcomes of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer following cell-free circulating tumor DNA genomic profiling.Lung Cancer. 2020 Oct;148:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.07.033. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32823229
-
Budget Impact Analysis of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2021 Nov;5:1611-1624. doi: 10.1200/PO.20.00540. JCO Precis Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34994647
-
Real-World Survival Outcomes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Impact of Genomic Testing and Targeted Therapies in a Latin American Middle-Income Country.JCO Glob Oncol. 2024 Dec;10:e2400338. doi: 10.1200/GO-24-00338. Epub 2024 Dec 5. JCO Glob Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39637345 Review.
-
Usefulness of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Clinical Decision-Making in Oncology: A Systematic Review.J Immunother Precis Oncol. 2025 Jan 14;8(1):55-63. doi: 10.36401/JIPO-24-11. eCollection 2025 Feb. J Immunother Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39811425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarker Testing Approaches, Treatment Selection, and Cost of Care Among Adults With Advanced Cancer.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 Jul 1;8(7):e2519963. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.19963. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 40643914 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor diagnosis recharacterization enabled by comprehensive genomic profiling to guide precision medicine strategy.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 May 21;9(1):149. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-00942-5. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40399445 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing immunotherapy for lung cancer: integrating genetic alterations and the tumor mutational burden to refine patient selection.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 31;14(1):29-32. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1734. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39974381 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A machine learning-based analysis of nationwide cancer comprehensive genomic profiling data across cancer types to identify features associated with recommendation of genome-matched therapy.ESMO Open. 2024 Dec;9(12):103998. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103998. Epub 2024 Nov 25. ESMO Open. 2024. PMID: 39591805 Free PMC article.
-
Toward Timely and Equitable Advanced Biomarker Testing for Patients with Metastatic Cancer in Canada.Curr Oncol. 2025 Feb 27;32(3):141. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32030141. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40136345 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

