A Novel Inhibitor of Translation Initiation Factor eIF5B in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 38755008
- PMCID: PMC11239407
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2404.04015
A Novel Inhibitor of Translation Initiation Factor eIF5B in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
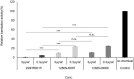
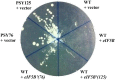
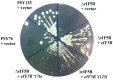
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF5B is a bacterial IF2 ortholog that plays an important role in ribosome joining and stabilization of the initiator tRNA on the AUG start codon during the initiation of translation. We identified the fluorophenyl oxazole derivative 2,2-dibromo-1-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)benzo[d]oxazol-5-yl)ethanone quinolinol as an inhibitor of fungal protein synthesis using an in vitro translation assay in a fungal system. Mutants resistant to this compound were isolated in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and were demonstrated to contain amino acid substitutions in eIF5B that conferred the resistance. These results suggest that eIF5B is a target of potential antifungal compound and that mutation of eIF5B can confer resistance. Subsequent identification of 16 other mutants revealed that primary mutations clustered mainly on domain 2 of eIF5B and secondarily mainly on domain 4. Domain 2 has been implicated in the interaction with the small ribosomal subunit during initiation of translation. The tested translation inhibitor could act by weakening the functional contact between eIF5B and the ribosome complex. This data provides the basis for the development of a new family of antifungals.
Keywords: Translation inhibitor; antifungal; eIF5B; target; translation initiation factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Interaction between the Ribosomal Stalk Proteins and Translation Initiation Factor 5B Promotes Translation Initiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Jul 30;38(16):e00067-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00067-18. Print 2018 Aug 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29844065 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between 25S rRNA A loop and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B promotes subunit joining and ensures stringent AUG selection.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;33(18):3540-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00771-13. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23836883 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation factor eIF5B catalyzes second GTP-dependent step in eukaryotic translation initiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 24;99(26):16689-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.262569399. Epub 2002 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12471154 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the transition from translation initiation to elongation by an 80S-eIF5B complex.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 6;11(1):5003. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18829-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33024099 Free PMC article.
-
Universal translation initiation factor IF2/eIF5B.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:417-24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2001.66.417. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001. PMID: 12762044 Review. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

