The nucleic acid binding protein SFPQ represses EBV lytic reactivation by promoting histone H1 expression
- PMID: 38755141
- PMCID: PMC11099029
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48333-x
The nucleic acid binding protein SFPQ represses EBV lytic reactivation by promoting histone H1 expression
Abstract
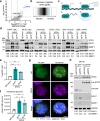
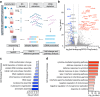
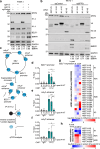
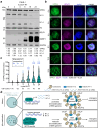
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) uses a biphasic lifecycle of latency and lytic reactivation to infect >95% of adults worldwide. Despite its central role in EBV persistence and oncogenesis, much remains unknown about how EBV latency is maintained. We used a human genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screen to identify that the nuclear protein SFPQ was critical for latency. SFPQ supported expression of linker histone H1, which stabilizes nucleosomes and regulates nuclear architecture, but has not been previously implicated in EBV gene regulation. H1 occupied latent EBV genomes, including the immediate early gene BZLF1 promoter. Upon reactivation, SFPQ was sequestered into sub-nuclear puncta, and EBV genomic H1 occupancy diminished. Enforced H1 expression blocked EBV reactivation upon SFPQ knockout, confirming it as necessary downstream of SFPQ. SFPQ knockout triggered reactivation of EBV in B and epithelial cells, as well as of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in B cells, suggesting a conserved gamma-herpesvirus role. These findings highlight SFPQ as a major regulator of H1 expression and EBV latency.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gewurz, B. E., Longnecker, R. & Cohen, J. I. Epstein-Barr virus. in Fields Virology, 7th edn (eds Knipe, D. & Howley, P.) 324–389 (Wolters Kluwer, 2021).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI170751/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 AI164709/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI162624/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007245/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI172329/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- F32 AI172329/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DE031016/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA275301/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI007245/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 CA228700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI164709/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- CA228700/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- P01 CA269043/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI170751/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DE031016/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 CA272142/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

