A novel family of defensin-like peptides from Hermetia illucens with antibacterial properties
- PMID: 38755524
- PMCID: PMC11097590
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-024-03325-1
A novel family of defensin-like peptides from Hermetia illucens with antibacterial properties
Abstract
Background: The world faces a major infectious disease challenge. Interest in the discovery, design, or development of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) as an alternative approach for the treatment of bacterial infections has increased. Insects are a good source of AMPs which are the main effector molecules of their innate immune system. Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) are being developed for large-scale rearing for food sustainability, waste reduction and as sustainable animal and fish feed. Bioinformatic studies have suggested that BSFL have the largest number of AMPs identified in insects. However, most AMPs identified in BSF have not yet undergone antimicrobial evaluation but are promising leads to treat critical infections.
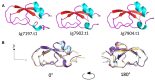
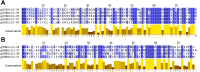
Results: Jg7197.t1, Jg7902.t1 and Jg7904.t1 were expressed into the haemolymph of larvae following infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and were predicted to be AMPs using the computational tool ampir. The genes encoding these proteins were within 2 distinct clusters in chromosome 1 of the BSF genome. Following removal of signal peptides, predicted structures of the mature proteins were superimposed, highlighting a high degree of structural conservation. The 3 AMPs share primary sequences with proteins that contain a Kunitz-binding domain; characterised for inhibitory action against proteases, and antimicrobial activities. An in vitro antimicrobial screen indicated that heterologously expressed SUMO-Jg7197.t1 and SUMO-Jg7902.t1 did not show activity against 12 bacterial strains. While recombinant SUMO-Jg7904.t1 had antimicrobial activity against a range of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, including the serious pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Conclusions: We have cloned and purified putative AMPs from BSFL and performed initial in vitro experiments to evaluate their antimicrobial activity. In doing so, we have identified a putative novel defensin-like AMP, Jg7904.t1, encoded in a paralogous gene cluster, with antimicrobial activity against P. aeruginosa.
Keywords: Hermetia illucens; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; AlphaFold; Antibiotics; Antimicrobial peptides; Black soldier fly larvae; Defensins.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MP and TG are current employees of Better Origin. The rest of the authors have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia Illucens) against a Selection of Human Pathogens.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0166421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01664-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 34985302 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterizations and heterogenous expression of the antimicrobial peptides, Hidefensins, from black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (L.).Protein Expr Purif. 2022 Apr;192:106032. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2021.106032. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Protein Expr Purif. 2022. PMID: 34922007
-
Multiple diptericins of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) differentially respond to bacterial challenges.J Invertebr Pathol. 2024 Nov;207:108234. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2024.108234. Epub 2024 Nov 13. J Invertebr Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39542086
-
Antimicrobial Peptides from Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Potential Antimicrobial Factors Representing an Alternative to Antibiotics in Livestock Farming.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jun 29;11(7):1937. doi: 10.3390/ani11071937. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insect antimicrobial peptides: potential weapons to counteract the antibiotic resistance.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(9):4259-4282. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03784-z. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33595669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-level biosynthesis and purification of the antimicrobial peptide Kiadin based on non-chromatographic purification and acid cleavage methods.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2025 Jan 16;18(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13068-025-02607-8. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2025. PMID: 39819334 Free PMC article.
-
Black Soldier Fly: A Keystone Species for the Future of Sustainable Waste Management and Nutritional Resource Development: A Review.Insects. 2025 Jul 22;16(8):750. doi: 10.3390/insects16080750. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40870551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of antimicrobial peptides in Hermetia illucens in response to fungal exposure.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 28;14(1):29561. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80133-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39609510 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

