Xpert HIV-1 qual point-of-care testing for HIV early infant diagnosis in Tanzania: experiences and perceptions of health care workers in a 2016 study
- PMID: 38755626
- PMCID: PMC11097447
- DOI: 10.1186/s12981-024-00619-2
Xpert HIV-1 qual point-of-care testing for HIV early infant diagnosis in Tanzania: experiences and perceptions of health care workers in a 2016 study
Abstract
Background: HIV early infant diagnosis (HEID) at the centralized laboratory faces many challenges that impact the cascade of timely HEID. Point of Care (PoC) HEID has shown to reduce test turnaround times, allow for task shifting and has the potential to reduce infant mortality. We aimed at assessing the feasibility of nurse based PoC-HEID in five facilities of Mbeya region.
Methods: We analysed data from healthcare workers at five obstetric health facilities that participated in the BABY study which enrolled mothers living with HIV and their HIV exposed infants who were followed up until 6 weeks post-delivery. Nurses and laboratory personnel were trained and performed HEID procedures using the Xpert HIV-1 Qual PoC systems. Involved personnel were interviewed on feasibility, knowledge and competency of procedures and overall impression of the use of HIV-1 Qual PoC system in clinical settings.
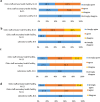
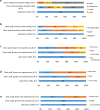
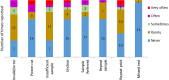
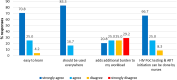
Results: A total of 28 health care workers (HCWs) who participated in the study between 2014 and 2016 were interviewed, 23 being nurses, 1 clinical officer, 1 lab scientist and 3 lab technicians The median age was 39.5 years. Majority of the nurses (22/24) and all lab staff were confident using Gene Xpert PoC test after being trained. None of them rated Gene Xpert handling as too complicated despite minor challenges. Five HCWs (5/24) reported power cut as the most often occurring problem. As an overall impression, all interviewees agreed on PoC HEID to be used in clinical settings however, about half of them (11/24) indicated that the PoC-HEID procedures add a burden onto their routine workload.
Conclusion: Overall, health care workers in our study demonstrated very good perceptions and experiences of using PoC HEID. Efforts should be invested on quality training, targeted task distribution at the clinics, continual supportive supervision and power back up mechanisms to make the wide-scale adoption of nurse based PoC HEID testing a possibility.
Keywords: Early infant diagnosis; HIV; Point-of-care testing; Primary healthcare workers; Vertical HIV transmission.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicting interests.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS Global AIDS Monitoring data, 2022. 2022;
-
- National guidelines for the management of HIV and AIDS, The United Republic of Tanzania 2019(255):1–16.
-
- WHO. Hiv Prevention, Infant Diagnosis, Antiretroviral Initiation and Monitoring Guidelines. 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

