Searching for the social determinants of health: observations from evidence synthesis publications
- PMID: 38755700
- PMCID: PMC11097542
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-024-02551-y
Searching for the social determinants of health: observations from evidence synthesis publications
Abstract
Background: The social determinants of health (SDOH) are the focus of an exponentially increasing number of publications, including evidence syntheses. However, there is not an established standard for searching for SDOH literature. This study seeks to identify published evidence syntheses pertaining to the SDOH, analyzing the search strategies used and the studies included within these reviews. The primary objectives are to compare search strategies and create a test set of SDOH publications.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and Scopus for evidence syntheses that mentioned the SDOH in their research questions and included an SDOH search strategy. Relevant data extracted from each review included databases searched; search terms used for the SDOH; conceptual frameworks referenced; and the citations of primary studies included in the reviews, which were compiled to form a test set of cited papers. The relative recall of the respective search strategies was tested by documenting the total number of MEDLINE results each retrieved and the number of test set papers retrieved.
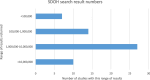
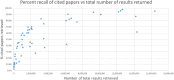
Results: Sixty-four evidence syntheses were identified and included in the analysis, and 2750 cited papers were extracted. Findings indicate few commonalities across search strategies in search terms used, the total number of results retrieved, and the number of test set cited papers retrieved. One hundred and ninety-three unique MeSH terms and 1385 unique keywords and phrases were noted among the various search strategies. The number of total results retrieved by the SDOH search strategies ranged from 21,793 to over 16 million. The percentage of cited papers retrieved by the search strategies ranged from 2.46 to 97.9%. Less than 3% of the cited papers were indexed with the Social Determinants of Health MeSH.
Conclusions: There has been little consistency across evidence syntheses in approaches to searching for SDOH literature. Differences in these strategies could have a significant impact on what literature is retrieved, included in reviews, and, consequently, incorporated into evidence-based practice. By documenting these differences and creating a set of papers relevant to SDOH, this research provides a snapshot of the current challenges in searching for SDOH content and lays the groundwork for the creation of a standardized search approach for SDOH literature.
Keywords: Evidence synthesis; Evidence-based public health; Health equity; Information search and retrieval; Review literature as topic; Social determinants of health; Systematic reviews.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Information sources for obesity prevention policy research: a review of systematic reviews.Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 8;6(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13643-017-0543-2. Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28789703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Representation of Social Determinants of Health terminology in medical subject headings: impact of added terms.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2024 Nov 1;31(11):2595-2604. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocae191. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39047296 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementary strategies identified additional eligible studies in qualitative systematic reviews.J Clin Epidemiol. 2023 Jul;159:85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2023.04.017. Epub 2023 May 17. J Clin Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 37201687
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Social determinants of health in electronic health records and their impact on analysis and risk prediction: A systematic review.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020 Nov 1;27(11):1764-1773. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa143. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020. PMID: 33202021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Social determinants of malaria in low- and middle-income countries: a mixed-methods systematic review.Malar J. 2025 May 26;24(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12936-025-05407-5. Malar J. 2025. PMID: 40420124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of LGBTQIA+ search filters: report on process and pilot filter for queer women.J Med Libr Assoc. 2025 Apr 18;113(2):123-132. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2025.2002. J Med Libr Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40342307 Free PMC article.
-
Putting All Our Eggs in One Basket While Dancing Around the Elephant in the Room: How Health and Economy Conversations Need to Better Align.Health Promot J Austr. 2025 Jul;36(3):e70050. doi: 10.1002/hpja.70050. Health Promot J Austr. 2025. PMID: 40304229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhat AA, Rashid I, Hassan SU, Kansra P. Social determinants of health and health outcomes: a bibliographic review of the scientific literature from 2000 to 2021. Glob Knowl Mem Commun. 2023;ahead of print. 10.1108/GKMC-09-2022-0214.
-
- Luo X, Wang S, Pu H, Long C, Ren Z, Lai Y. Knowledge mapping and research trends of the social determinants of health (SDoH): a scientometric analysis. Rev Environ Health. Published online February 8, 2023. 10.1515/reveh-2022-0186. - PubMed
-
- Commission on Social Determinants of Health. Closing the gap in a generation: health equity through action on the social determinants of health. Final Report of the Commission on Social Determinants of Health. World Health Organization; 2008. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/43943/9789241563703_eng....
-
- Healthy People 2030 Framework - Healthy People 2030. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Accessed June 14, 2022. https://health.gov/healthypeople/about/healthy-people-2030-framework.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources