The most fundamental and popular literature on functional near-infrared spectroscopy: a bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most cited articles
- PMID: 38756218
- PMCID: PMC11096499
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1388306
The most fundamental and popular literature on functional near-infrared spectroscopy: a bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most cited articles
Abstract
Background: Functional near infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) has developed rapidly in recent years, and there are more and more studies on fNIRS. At present, there is no bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most cited articles on fNIRS research.
Objective: To identify the top 100 most cited articles on fNIRS and analyze those most fundamental and popular articles through bibliometric research methods.
Methods: The literature on fNIRS of web of science from 1990 to 2023 was searched and the top 100 most cited articles were identified by citations. Use the bibliometrix package in R studio and VOSviewer for data analysis and plotting to obtain the output characteristics and citation status of these 100 most cited articles, and analyze research trends in this field through keywords.
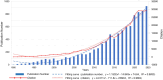
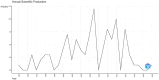
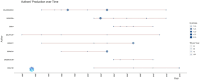
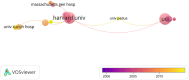
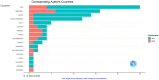
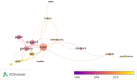
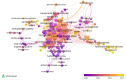
Results: A total of 9,424 articles were retrieved from web of science since 1990. The average citation number of the 100 articles was 457.4 (range from 260 to 1,366). Neuroimage published the most articles (n = 31). Villringer, A. from Leipzig University had the largest number of top 100 papers. Harvard University (n = 22) conducted most cited articles. The United States, Germany, Japan, and the United Kingdom had most cited articles, respectively. The most common keywords were near-infrared spectroscopy, activation, cerebral-blood-flow, brain, newborn-infants, oxygenation, cortex, fMRI, spectroscopy. The fund sources mostly came from National Institutes of Health Unitd States (NIH) and United States Department of Health Human Services (n = 28).
Conclusion: Neuroimage was the most popular journal. The top countries, institutions, and authors were the United States, Harvard University, and Villringer, A., respectively. Researchers and institutions from North America and Europe contributed the most. Near-infrared spectroscopy, activation, cerebral-blood-flow, brain, newborn-infants, oxygenation, cortex, fmri, spectroscopy, stimulation, blood-flow, light-propagation, infants, tissue comprise the future research directions and potential topic hotspots for fNIRS.
Keywords: activation; brain; cerebral-blood-flow; cortex; fMRI; near-infrared spectroscopy; newborn-infants; oxygenation.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Li, Huang, Li, Wan, Sun, Zeng, Xu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The top 100 highly cited articles on osteoporosis from 1990 to 2019: a bibliometric and visualized analysis.Arch Osteoporos. 2020 Sep 15;15(1):144. doi: 10.1007/s11657-020-0705-z. Arch Osteoporos. 2020. PMID: 32935223
-
Hotspots and trends in fNIRS disease research: A bibliometric analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 2;17:1097002. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1097002. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36937686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Top-Cited Original Articles on the Role of Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 5;14:869964. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.869964. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35478696 Free PMC article.
-
The top 100 highly cited articles on anterior cruciate ligament from 2000 to 2019: A bibliometric and visualized analysis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021 Dec;107(8):102988. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2021.102988. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34146752
-
Shedding light on neuroscience: Two decades of functional near-infrared spectroscopy applications and advances from a bibliometric perspective.J Neuroimaging. 2021 Jul;31(4):641-655. doi: 10.1111/jon.12877. Epub 2021 May 18. J Neuroimaging. 2021. PMID: 34002425 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and trends in the application of functional near-infrared spectroscopy for pediatric assessments: a bibliometric analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Sep 6;15:1459214. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1459214. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39309263 Free PMC article.
-
The role of fNIRS in assessing motor function: A bibliometric review on extremity applications.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 8;104(32):e43707. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043707. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40797442 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

