An Eco-Friendly Synthesis Approach for Enhanced Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Properties of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Coelastrella terrestris Algal Extract
- PMID: 38756417
- PMCID: PMC11096669
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S452889
An Eco-Friendly Synthesis Approach for Enhanced Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Properties of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Coelastrella terrestris Algal Extract
Abstract
Background: In the current scenario, the synthesis of nanoparticles (NPs) using environmentally benign methods has gained significant attention due to their facile processes, cost-effectiveness, and eco-friendly nature.
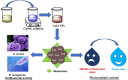
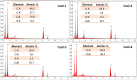
Methods: In the present study, copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) were synthesized using aqueous extract of Coelastrella terrestris algae as a reducing, stabilizing, and capping agent. The synthesized CuO NPs were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS).
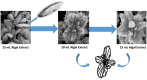
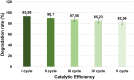
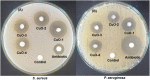
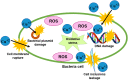
Results: XRD investigation revealed that the biosynthesized CuO NPs were nanocrystalline with high-phase purity and size in the range of 4.26 nm to 28.51 nm. FTIR spectra confirmed the existence of secondary metabolites on the surface of the synthesized CuO NPs, with characteristic Cu-O vibrations being identified around 600 cm-1, 496 cm-1, and 440 cm-1. The FE-SEM images predicted that the enhancement of the algal extract amount converted the flattened rice-like structures of CuO NPs into flower petal-like structures. Furthermore, the degradation ability of biosynthesized CuO NPs was investigated against Amido black 10B (AB10B) dye. The results displayed that the optimal degradation efficacy of AB10B dye was 94.19%, obtained at 6 pH, 50 ppm concentration of dye, and 0.05 g dosage of CuO NPs in 90 min with a pseudo-first-order rate constant of 0.0296 min-1. The CuO-1 NPs synthesized through algae exhibited notable antibacterial efficacy against S. aureus with a zone of inhibition (ZOI) of 22 mm and against P. aeruginosa with a ZOI of 17 mm.
Conclusion: Based on the findings of this study, it can be concluded that utilizing Coelastrella terrestris algae for the synthesis of CuO NPs presents a promising solution for addressing environmental contamination.
Keywords: CuO NPs; antibacterial activity; green synthesis; photocatalysis; wastewater treatment.
© 2024 Khandelwal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures














Similar articles
-
Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Abutilon indicum leaves extract and their evaluation of antibacterial, anticancer in human A549 lung and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.Food Chem Toxicol. 2022 Oct;168:113330. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113330. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35926645
-
Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its efficiency in degradation of rifampicin antibiotic.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 28;13(1):14030. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41119-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37640783 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using gum karaya as a biotemplate and their antibacterial application.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:889-98. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S40599. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23467397 Free PMC article.
-
Eco-friendly copper nanoparticles embedded cellulose aerogel from corn husk with robust antibacterial and catalytic reduction performance.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;310(Pt 2):143359. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.143359. Epub 2025 Apr 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40258545 Review.
-
Harnessing plant extracts for eco-friendly synthesis of iron nanoparticle (Fe-NPs): Characterization and their potential applications for ameliorating environmental pollutants.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Aug;281:116620. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116620. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 38905935 Review.
Cited by
-
Facile fabrication of a novel chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose/bentonite/CuO nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial applications.RSC Adv. 2025 Feb 3;15(5):3365-3377. doi: 10.1039/d4ra08437c. eCollection 2025 Jan 29. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 39902111 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in phyto- and microorganisms-mediated synthesis of copper nanoparticles and their emerging applications in healthcare, environment, agriculture and food industry.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025 Jul 9. doi: 10.1007/s00449-025-03196-4. Online ahead of print. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025. PMID: 40632213 Review.
References
-
- Wijesinghe U, Thiripuranathar G, Iqbal H, Menaa F. Biomimetic synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of fluorescence resonance energy transfer, photoluminescence, and photocatalytic activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Sustainability. 2021;13(4):2004. doi:10.3390/su13042004 - DOI
-
- Aravind M, Amalanathan M, Mary M. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by chemical and green synthesis methods and their multifaceted properties. SN Appl Sci. 2021;3(4):1–10. doi:10.1007/s42452-021-04281-5 - DOI
-
- Khandelwal M, Kumawat A, Misra KP, Khangarot RK. Efficient antibacterial activity in copper oxide nanoparticles biosynthesized via Jasminum sambac flower extract. Part Sci Technol. 2022;2:1–13.
-
- Siddique AB, Amr D, Abbas A, et al. Synthesis of hydroxyethylcellulose phthalate-modified silver nanoparticles and their multifunctional applications as an efficient antibacterial, photocatalytic and mercury-selective sensing agent. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;256:128009. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128009 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

