Brain Abscess due to Streptococcus intermedius after Spontaneous Esophageal Perforation in an Adolescent
- PMID: 38756504
- PMCID: PMC11098600
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/5593403
Brain Abscess due to Streptococcus intermedius after Spontaneous Esophageal Perforation in an Adolescent
Abstract
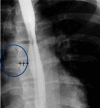
Streptococcus intermedius is an inhabitant of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract, known to cause deep-seated abscesses. Thereby, we present a previously healthy adolescent with esophageal perforation (EP) and secondary mediastinal and brain abscesses due to Streptococcus intermedius. EP is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires a prompt diagnosis.
Copyright © 2024 Sandra Mabel Camacho-Gomez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Camacho-Gomez, Monagas, and Noel have disclosed no financial relationships relevant to this article. Dr. Castagnini works for Merck Research Laboratories; he has disclosed no financial relationships relevant to this article.
Figures



References
-
- Committee on Infectious Diseases. American academy of pediatrics. Section 3: summaries of infectious diseases. Non-group A or B streptococcal and enterococcal infections. In: Kimberlin D. W., Brandy M. T., Jackson M. A., Long S. S., editors. Red Book: 2018 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases . Itasca, IL, USA: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2018. pp. 768–772.
-
- Whiley R. A., Beighton D., Winstanley T. G., Fraser H. Y., Hardie J. M. Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus (the Streptococcus milleri group): association with different body sites and clinical infections. Journal of Clinical Microbiology . 1992;30(1):243–244. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.243-244.1992. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whiley R. A., Fraser H., Hardie J. M., Beighton D. Phenotypic differentiation of Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus strains within the Streptococcus milleri group. Journal of Clinical Microbiology . 1990;28(7):1497–1501. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1497-1501.1990. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

