PD-L1 expression in pancreaticobiliary adenosquamous carcinoma: a single-institution case series
- PMID: 38756636
- PMCID: PMC11094501
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-24-9
PD-L1 expression in pancreaticobiliary adenosquamous carcinoma: a single-institution case series
Abstract
Background: The programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) pathway is a potent negative regulator of T-cell-mediated immune response that is upregulated in many neoplasms. Pancreaticobiliary adenosquamous carcinoma (PB-ASC) is an aggressive cancer that carries a poorer prognosis compared with pure pancreaticobiliary adenocarcinoma (PB-AC). To date, there is little published information regarding PD-L1 expression in PB-ASC. The aim of the study was to examine the relationship between PD-L1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in PB-ASC and PB-AC.
Methods: We evaluated 15 PB-ASCs (10 pancreatic, 5 gallbladder) and 34 control PB-ACs (22 pancreatic ductal, and 12 gallbladder) for tumor expression of PD-L1 using anti-PD-L1 (E1L3N) antibody. All tumors were classified into three immune phenotypes: immune inflamed (II), immune excluded (IE), and immune desert (ID) according to the distribution of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in tumor tissues.
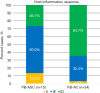
Results: The frequency of PD-L1 expression was significantly higher in PB-ASC (10/15; 66.7%) than in PB-AC (3/34; 8.8%). In PB-ASC, PD-L1 expression occurred exclusively in the squamous component in six cases, exclusively in the glandular component in one case, and in both the squamous and the glandular components in three cases. PD-L1 expression in PB-ASC was irrespective of the tumor immune status, whereas its expression in PB-AC was observed only in tumors with the II or IE phenotype. The ID phenotype was relatively rare (4/15; 26.7%) in PB-ASC compared with PB-AC (22/34; 65%; P=0.02).
Conclusions: PB-ASCs are notably enriched in inflammatory response and showed significantly higher PD-L1 expression than PB-AC (P<0.001), suggesting a potential therapeutic role for immune checkpoint inhibitors in managing patients with PB-ASC.
Keywords: Pancreaticobiliary carcinoma; adenosquamous carcinoma (ACC); programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1); squamous differentiation; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs).
2024 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-24-9/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Comment in
-
PD-L1 expression in pancreaticobiliary adenosquamous carcinoma: a potential biomarker for immunotherapy.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Aug 31;15(4):2011-2012. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-554. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39279971 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog and programmed cell death ligand 1 in adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 18;503(4):2764-2769. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.037. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30100056
-
Heterogeneity of tumor immune microenvironment and real-world analysis of immunotherapy efficacy in lung adenosquamous carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 12;13:944812. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.944812. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032124 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes status, programmed death-ligand 1 expression, and clinicopathological features of 41 cases of pure apocrine carcinoma of the breast: a retrospective study based on clinical pathological analysis and different immune statuses.Gland Surg. 2022 Jun;11(6):1037-1046. doi: 10.21037/gs-22-248. Gland Surg. 2022. PMID: 35800740 Free PMC article.
-
Use of sintilimab in primary adenosquamous carcinoma of the liver results in pathological complete response: a case report and literature review.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1578368. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1578368. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40370460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of evaluating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in breast cancer.Med Mol Morphol. 2017 Dec;50(4):185-194. doi: 10.1007/s00795-017-0170-y. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Med Mol Morphol. 2017. PMID: 28936553 Review.
Cited by
-
PD-L1 expression in pancreaticobiliary adenosquamous carcinoma: a potential biomarker for immunotherapy.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Aug 31;15(4):2011-2012. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-554. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39279971 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (5th ed). WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System, vol. 1. Lyon: IARC; 2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
