The oxidant-antioxidant imbalance was involved in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
- PMID: 38756779
- PMCID: PMC11096511
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1380846
The oxidant-antioxidant imbalance was involved in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
Abstract
Background: Although oxidative stress is involved in the pathophysiological process of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP), the specific underlying mechanism is still unclear. Whether antioxidant therapy can treat CRSwNP needs further investigation.
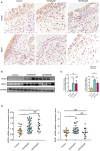
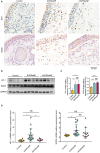
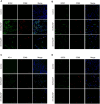
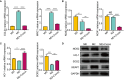
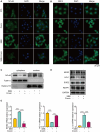
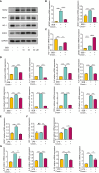
Methods: Immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, western blotting and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analyses were performed to detect the distribution and expression of oxidants and antioxidants in nasal polyp tissues. qPCR revealed correlations between oxidase, antioxidant enzymes and inflammatory cytokine levels in CRSwNP patients. Human nasal epithelial cells (HNEpCs) and primary macrophages were cultured to track the cellular origin of oxidative stress in nasal polyps(NPs) and to determine whether crocin can reduce cellular inflammation by increasing the cellular antioxidant capacity.
Results: The expression of NOS2, NOX1, HO-1 and SOD2 was increased in nasal epithelial cells and macrophages derived from nasal polyp tissue. Oxidase levels were positively correlated with those of inflammatory cytokines (IL-5 and IL-6). Conversely, the levels of antioxidant enzymes were negatively correlated with those of IL-13 and IFN-γ. Crocin inhibited M1 and M2 macrophage polarization as well as the expression of NOS2 and NOX1 and improved the antioxidant capacity of M2 macrophages. Moreover, crocin enhanced the ability of antioxidants to reduce inflammation via the KEAP1/NRF2/HO-1 pathway in HNEpCs treated with SEB or LPS. Additionally, we observed the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of crocin in nasal explants.
Conclusion: Oxidative stress plays an important role in the development of CRSwNP by promoting various types of inflammation. The oxidative stress of nasal polyps comes from epithelial cells and macrophages. Antioxidant therapy may be a promising strategy for treating CRSwNP.
Keywords: CRSwNP; Nrf2; macrophages; nasal epithelial cells; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Zhou, Liu, Liu, Meng, Wen, Luo, Liu, Li, Ba and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ADAM28 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition and impairs tight junctions in non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps by inducing M1 polarization of macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Mar 26;150:114276. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114276. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39954661
-
Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family 8 disrupts epithelial barrier in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps through M1 macrophage polarization.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025 Apr;134(4):431-441.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2025.01.020. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39870212
-
Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: modulation by cytokines.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015 Aug;5(8):734-40. doi: 10.1002/alr.21530. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. PMID: 25907676
-
Cytokine Signature and Involvement in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 30;23(1):417. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010417. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B-Cells and Antibody-Mediated Pathogenesis in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;79:48-57. doi: 10.1159/000445129. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 27466846 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in otorhinolaryngological diseases: insights from pathophysiology to targeted antioxidant therapies.Redox Rep. 2025 Dec;30(1):2458942. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2025.2458942. Epub 2025 Feb 2. Redox Rep. 2025. PMID: 39894944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of sestrin-2 levels and thiol-disulfide homeostasis in polyp tissue of patients with nasal polyps.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 26;15(1):14615. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95453-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40287482 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

